

- BLOG
Challenges of Indoor Logistics: Routing From the Last Mile to the Last Meter
Published: October 23, 2025
Route Optimization API
Optimize routing, task allocation and dispatch
Distance Matrix API
Calculate accurate ETAs, distances and directions
Directions API
Compute routes between two locations
Driver Assignment API
Assign the best driver for every order
Routing & Dispatch App
Plan optimized routes with 50+ Constraints
Product Demos
See NextBillion.ai APIs & SDKs In action
AI Route Optimization
Learns from Your Fleet’s Past Performance
Platform Overview
Learn about how Nextbillion.ai's platform is designed
Road Editor App
Private Routing Preferences For Custom Routing
On-Premise Deployments
Take Full Control of Your Maps and Routing
Trucking
Get regulation-compliant truck routes
Fleet Management
Solve fleet tracking, routing and navigation
Middle Mile Delivery
Optimized supply chain routes
Construction
Routes for Construction Material Delivery
Oil & Gas
Safe & Compliant Routing
Food & Beverage
Plan deliveries of refrigerated goods with regular shipments
Table of Contents

The statistical by Forbes found that over 20.1% of the retail sales in the year 2024 were conducted online. It is convenient for the buyers to review the item details on an online portal. They can order it and receive the package at a chosen delivery location.
The ease of reaching far-off customers is transforming the buyer’s preferences. But at the same time, growing demands in this segment have instigated the companies to expand their serviceable area. While some are collaborating with investors, there are new investments pouring in from organized business groups.
The increasing competition in the logistics business, has made it evident for the companies to commit maximum value for money. Hence, the courier service providers have started focusing on last meter delivery management instead of following the traditional format of last mile delivery.
But what is last mile delivery, and last meter delivery service? How should you interpret the market shift in industry-specific transportation systems while inspecting the obstacles in delivering high-end services? Can AI-enabled technological systems offer accurate navigational assistance to the delivery agents such that they reach the customers for doorstep deliveries?
Let’s find out!
Last mile delivery is the concept of delivering the parcels at the customer’s location. It is the final step in the logistics system that completes the order for the customer.
The primary objective of an online order or a courier placement is to transit the products from the selling point or ordered station to the end location. The ordered boxes with consignment numbers are segregated based on the delivery locations and loaded on the transport vehicles to reach the next center.
Read: Vehicle tracking systems: what they are and why you need one?
Except for the online food delivery services, the logistics transport process usually involves multiple sections of pickups and drop-offs between warehouses. Hub stations nearest to the customer’s location complete the last mile delivery procedures by assigning the designated drivers in the area to distribute all the orders within the scheduled time.
Last mile logistics gained relevance after the eCommerce boom in the marketing channels. Internet speed has a major share in enhancing communication between cities and continents to form a global supply chain. Companies prepared to eliminate geographical boundaries by establishing an online presence and attracting customers from around the globe.
While the service is critical for customer satisfaction, there are multiple other factors that make last mile deliveries considerable for logistics.
Read how supply chain route optimization works.
Transportation systems, whether through road networks or sea routes, are the nerves behind every business that sells goods to organizations or individuals. But mostly the B2C market has to be concerned with the last mile delivery services.
Carriers handling bulk freight or raw materials for factories and manufacturing hubs are not always concerned with final transit. Rather, in such cases, the prime focus is on safe and steady movements to deliver the products successfully.
So, who really seeks commitment from delivery sectors to reach the location in a specific time slot?
E-Commerce segment:
Online shopping stores commit to deliver the products within a scheduled time. The majority of them accept cancellation or returns in case of damage or late services. To avoid such instances, these stores manage last mile deliveries effectively.
Online food orders:
It is essential for restaurants and food chains to receive online orders from local customers. Late deliveries or dismantled boxes in this case may lead to order cancelation and loss of reputation.
Courier:
Common people sending gift parcels to their loved ones or offices sending documents to a client use courier services. These companies calculate the end-to-end delivery route and ensure the customer receives the product at a certain time. Late or broken deliveries are considered unprofessional, leading to loss of business.
Grocery stores:
Online grocery stores or local retailers accept orders for home deliveries. Inventory and instant delivery are two major factors that proportionate online grocery business. Hence, serving deliveries in guaranteed time to the consumers establishes the brand.
Healthcare products:
People ordering medicines or healthcare equipment are often in critical condition and need them urgently. The last mile delivery system makes it possible by navigating the drivers to quickly pick up the orders and reach the destination in time.
Urban logistics system:
Transporting goods to the micro fulfillment centers in the urban areas is a typical example of last mile delivery. Products like milk, newspapers, and many others require last mile delivery optimization.
Also read: How ETA and ETD impact routing in logistics and transport?
Online marketing options with purchase and delivery solutions played a key role for the logistics industry to expand with multiple hubs, regional centers, and substations. Road networks, GPS systems, and trained staff members made it possible for the companies to reach buyers in time.
Last mile delivery is definitely a part of trust-building efforts, and hence, it has taken precedence in the delivery process.
Now the global logistics and transportation business is witnessing a transitional shift from the conventional last mile to the last meter delivery management.
But what is last meter delivery, and how does it impact the logistical industry?
Well, it is the formula upgrade in the delivery services. The idea of last meter delivery is to recognize the customer’s requirements while receiving the order and fulfill them with the highest potential.
In the last meter delivery mechanism, the agents can go an extra mile to reach the actual location of the customer. They reach the doorstep of the buyer instead of leaving the box at the building’s facility office. Due to delivery agents accessing the inner premises of the building, the companies have termed it as an indoor logistical challenge.
Transit companies enduring last meter delivery procedures train the drivers to navigate corridors, elevators, security systems, and multiple units. The purpose is to ensure the package arrives exactly at the recipient’s true destination, such as a specific office, apartment, or internal locker.
Also read: How to reduce last mile delivery costs using AI technology.
Online marketers are competing at global levels. They cannot afford to compromise on service quality, as it may result in losing customers’ loyalty. Last meter delivery is not the condition to survive in the current scenario but a choice to upgrade services and gain more customers.
There are several advantages of adding the indoor logistics option to your delivery services.
Customers’ expectation:
Last meter delivery service turns out to be a lucrative deal for the customers because companies offer to hit their doorbell and deliver the goods directly. The customers fo not have to worry about the safety and security of the items, as the parcel doesn’t reach the destinations through undesirable channels. It improves the company’s reputation, and the satisfied customers stay loyal to the brand.
Precise Instructions:
For achieving last meter delivery success, the dispatch managers provide sufficient instructions to the drivers, which assist them in locating the customers. With proper management of delivery schedules, the managers generate feasible ETAs and ETDs, which are essential for optimum loading and task scheduling.
Reduced failed delivery:
Sometimes the customers do not provide proper addresses, or they are located in a crowded region, which is hard to find. These orders often end up in failed delivery attempts and get cancelled. But in last meter attempts, the extra effort done by the on-spot drivers to reach the exact location ensures delivery success.
Resolve failed delivery attempts in 2025.
Regional competition:
Transit companies going the extra mile for hand-to-hand delivery of orders significantly enhance the customer relationship. The consistency in task completion generates customers’ preferences to buy from a particular company.
Work efficiency:
The delivery drivers are assigned the task with complete navigation and optimized routes. It is to help them reach the destination within the scheduled time and not waste fuel and energy in locating the place. This in turn improves work efficiency and success rate.
Software solution:
It has a positive impact on the companies considering indoor logistics, as they cannot avoid integrating advanced technological systems in the delivery process. It may initially cost you a lot financially, but soon it starts reducing costs with improved work efficiency.
People make online purchases with an aim to get the products at their doorsteps. They expect the delivery partners to make all the efforts and reach the exact location, even if their place is not easily accessible or it is across the restrictions of the building. The logistics companies do their best to fulfill the expectations of indoor logistics at the same rate or charge minimally.
But the process can be tiring and complex for both the route dispatch managers and the delivery staff. Below are a few prominent issues faced in last meter delivery completion.
Also read: What It Takes to Create an In-House Delivery System?
Logistics companies are offering services up to the last meter and touching the point of delivery. The purpose is to hand over the product to the actual buyer instead of submitting it at common spaces.
Considering the complexities and challenges of the task, it is essential to deploy resources that can help amplify the potential of the delivery team, thereby ensuring 100% success.
The experts at NextBillion.ai have rigorously analyzed the requirements of the logistics and transportation industry. Our powerful API solutions are capable of handling large volumes of data and automating the delivery procedures from load assessment to final drop-offs.
Read how NextBillion API optimizes load in delivery vehicles.
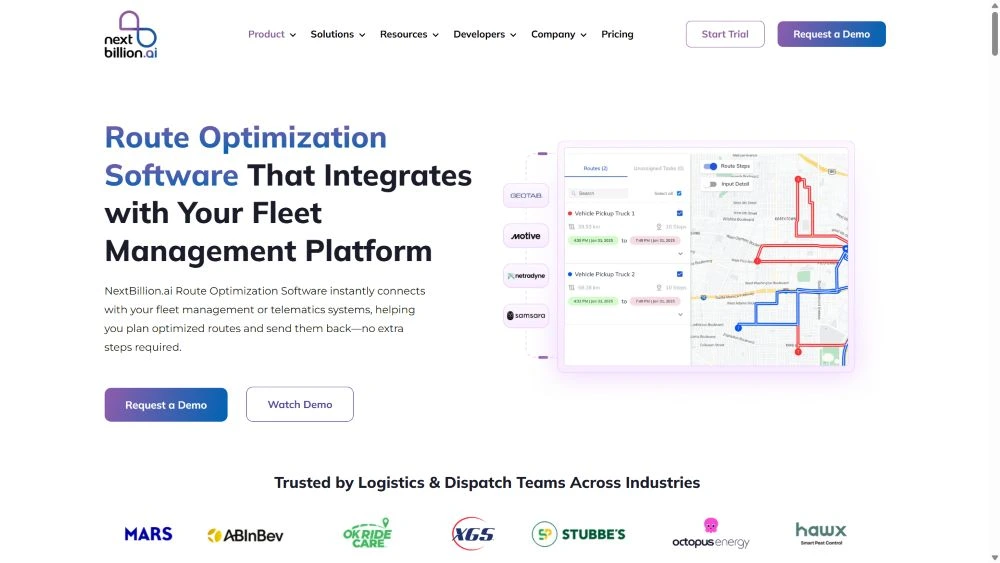
NextBillion’s route optimization software is compatible with all sorts of ERP datasets and real-time traffic data for accurate routing. It utilizes AI technology for quick analysis of the tasks to generate pathways that are feasible, easily accessible for the vehicles, and fuel efficient. Dispatchers can select the best route between the fastest and the shortest.
The tool focuses on precision routing with added features like advanced mapping. live tracking, or ease of operation that readily takes the responsibility of task completion.
We are providing a wide range of API integrations on the dashboard to manage logistics transport from last mile delivery to last meter delivery. The tools listed below prove highly effective for the delivery team for locating the exact destination of the package.
Route optimization API is the most demanded tool in the logistics industry. The delivery sector requires a tool that can instruct the drivers to move in a specific path and reach the destination. This API helps avoid route repetition, calculates accurate ETAs, and serves the purpose with the highest efficiency. It can customize the plans based on multiple constraints like travel time, maximum charges, order groups, zones, distance, etc.
The driver assignment API is essential for the allotment of delivery agents on the basis of their shifts, availability, skills, and requirements based on the specificity of the task. It is programmed in a way to enhance the work efficiency with feasible transportation and task management.
The clustering API is designed to undertake scenarios like indoor logistics. It analyzes all the delivery order data scheduled for the same or next day and if it has reached the warehouse. After examining the possibility of sending out the packages in a particular area, the tool creates clusters or groups for task implementation.
The directions API has the small purpose of finding the best route between two delivery locations. It calculates the total distance and generates an ETA.
Directions API vs Distance Matrix API
The distance matrix API provides a quick calculation of the distance between a large matrix of locations on the route. The distance is accurate even inside a building to support indoor logistics.
Also read: 5 best Distance Matrix APIs to try in 2025.
Snap-to-Road API takes a snapshot of different locations on a road network to analyze the most efficient route possible that covers all the required drop points.
The isochrones API calculates the delivery locations that have the same distance from a certain point and can be touched in the same time frame.
Navigation API are among the most essential tools in the route optimization mechanism. It will provide clear instructions to the delivery staff on the road network as well as inside the campus of the building. The precision of this navigation system directs the agents to the elevators, through the corridors, and to the exact location of the customer.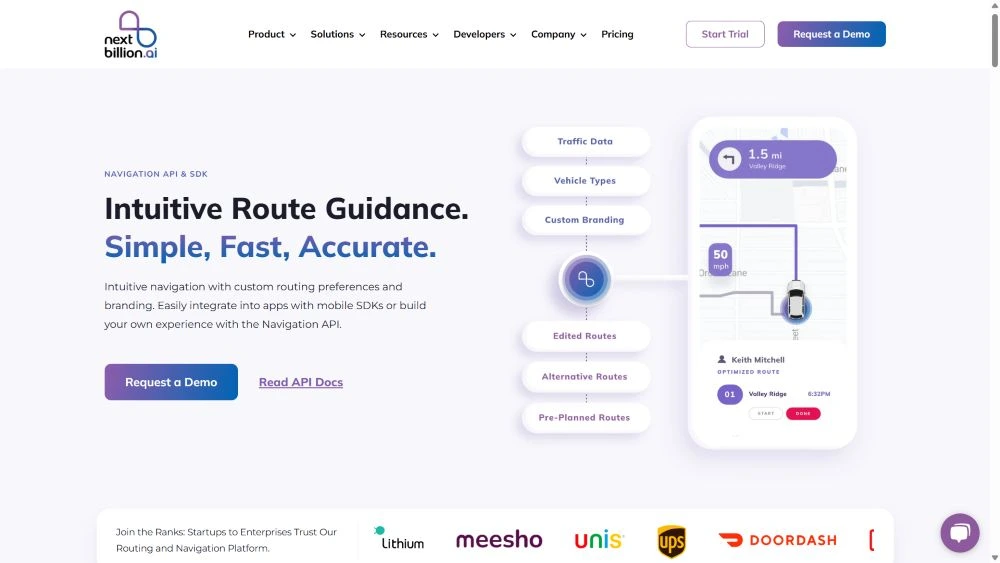
Read: 10 Best Navigation APIs/SDKs
The route report API is advantageous in making every future delivery assignment easier and more efficient. The tool gives an option to add journey details like road segments, speed, turns, tolls, etc. Now each new route plan will be generated after considering the report analysis.
The batch routing API enables the users to enter multiple routing requests and generate the plan at once. It helps calculate multiple isochrones in a single batch and is beneficial for managing the bulk of tasks in a dense area or building.
Live Tracking API is definitely a useful tool for logistics companies. It enables locating the delivery drivers at any given point on the route in real-time. The GPS system is the root of live tracking the movement on the map, which transmits the information in the network.
The geofence API creates a virtual fence for the delivery drivers. It can thus control the movement of delivery staff in and around a certain region and thereby save time and fuel wastage.
Read: What is geofencing; type, components, and application?
Check out how grocery delivery companies optimize route operations with geofencing.
Route reconstruction API can recreate the path taken by a delivery driver to finish the task. Once you provide the waypoints or locations covered, it can trace the entire route with the total distance travelled and whether it was one way or a round trip.
The route dispatch API is the step to forward the optimized route plan to the delivery drivers. It comprises all the delivery instructions, task details, and delivery proof document attached with the route plan.
Read about challenges related to dispatch management.
The documents API enables creating and attaching a short form with the dispatch order. It can have multiple fields and can be used as proof of delivery details or for recording information related to the trip.
The maptiles API has a unique functionality in mapping the delivery locations. It integrates image files of the area, societies, and complexes to complete the last meter delivery successfully. The image is in a grid format to expand for elaborated results.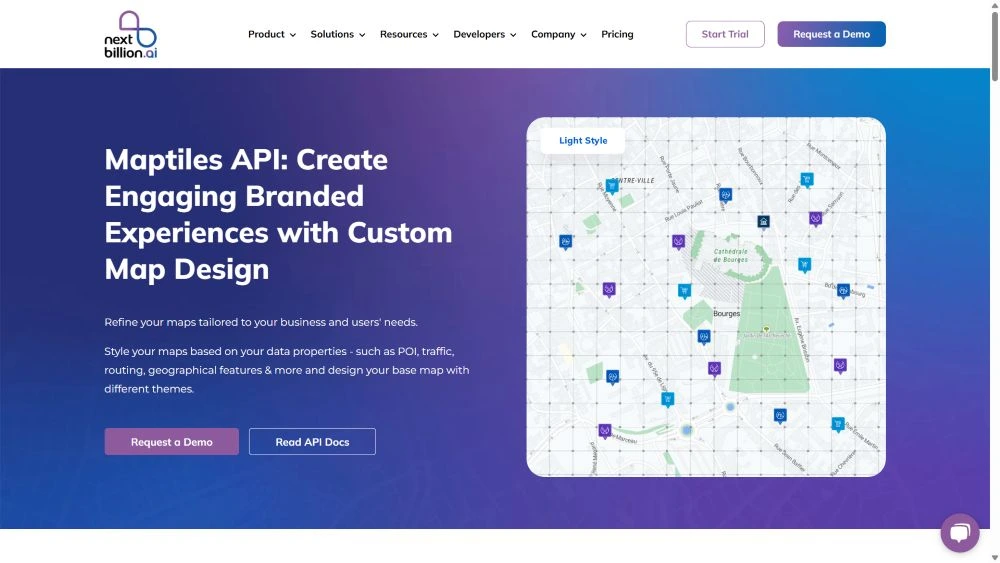
Read: What is a map tile; components, and advantages
The road segment API provides necessary information about the road network enclosed in a geographical area, and it may include the shape, size, lanes, midpoints, speed limits, etc.
The road editor API is a useful tool for dispatchers, as they can edit the routes and add specific instructions for the drivers, such as road restrictions, max speed, turns, tolls, etc.
Places API is a tool that can extract detailed information about the location. The features of the places API tool are highly beneficial in indoor logistics. With a range of functions, it can generate coordinates of places, or detailed addresses and postal codes out of coordinates.
It can batch process large data to geocode multiple addresses in a building and route for last meter delivery.
Last meter or indoor delivery service is an extension of the last mile operations. Similar to the complex road networks coupled with hindrances and halts, the indoor logistics also become tiresome for the delivery agents. Without instruction, they get confused, face multiple restrictions, and waste time reaching specific floors and flats.
The dashboard of the NextBillion route optimization API is empanelled with multiple tools that serve diverse functions. You can calculate ETAs, sequence delivery location routes inside a building, create efficient movements, or batch process bulk orders within seconds. By integrating the NextBillion API, you can easily manage last meter deliveries with the highest accuracy and customer satisfaction.
The integration of GPS and a mapping system with route optimization enhanced the delivery procedures. It assisted the drivers with pre-planned routes and sequences of operations.
Now there are powerful routing tools equipped with advanced AI technology. Tools like NextBillion can efficiently extract indoor data of the complex and assist navigation through the permitted area for the service personnel to reach the customer’s doorstep.
Last meter logistics deliveries are more challenging than transiting on crowded highways and complicated road networks. The delivery person has to face regulatory issues inside the societies and look for ways to travel through the permitted region.
NextBillion combines technology with human potential. It generates accurate paths for each point of delivery and keeps track of the servicemen to modify their direction if required.
Technology is currently the backbone of logistics and transport, as it speeds up the whole process, and optimized routes save time and fuel. Tools like route optimization, navigation, geofencing, alert systems, and live tracking are a great help in deploying the agents and fast-tracking the delivery process.
There are some key differences between last mile and last meter delivery systems.
While the end point in the last mile is the customer’s building or gate, in the last meter the end point is the flat’s doorstep inside the building.
In the last mile, the drivers are routed from the hub to the customer’s area; in the last meter, they are navigated from the hub to the elevator and till the customer’s door.
The main challenge in the last mile is traffic, routes, and schedules; in the last meter, the challenge is to get the access code and correct apartment.
The key technology in the last mile is GPS and a route planner; in the last meter, it is an indoor navigation system. 5 best route planner apps for android in 2025.
Majority of the companies serving deliverable products in the urban region benefit the most with last meter services. These may include e-commerce, pharmacy, grocery, courier, or B2B transition.
Powerful API solutions optimize the movement of delivery agents inside the building which leads to minimal failed delivery attempts. Additionally, the swift navigation, automated proof of delivery, and bulk order management reduces work pressure with efficient results.
Nitesh Malviya is a research-oriented professional with a background in Computer Science & Engineering. He served for 7 years as a software consultant and wrote passively in the tech niche before becoming a full-time technical writer.