Table of Contents
Mapbox is an industry leader in web and mobile map rendering technology, and it is renowned for offering developers, businesses, and business executives scalable, dependable, and highly performant location services. Global map data, real-time traffic, geocoding, address search, routing, and navigational guidance are all included in Mapbox services. Mapbox, which is free to start using and has monthly usage fees, is made for companies of all sizes. No upfront licenses or contracts are needed.
While Mapbox provides comprehensive features, there are other Mapbox alternatives in the market offering the same or more enhanced features in terms of functionality, scalability, and customization.
So, let’s focus on the following sections, where I will walk you through the advantages and disadvantages of Mapbox and give you a solution and better understanding to choose an alternative service.
Key Factors to consider when choosing Mapbox Alternatives and Competitors
Factor 1 – Cost: Mapbox follows a freemium pricing model with a generous free tier. However, costs can escalate quickly for high-volume usage. Some alternatives may offer more cost-effective pricing structures or even free options to specific use cases.
Factor 2 – Customization Limitations: You may sometimes find Mapbox provides restrictive customization tools compared to its alternatives in offering greater flexibility, such as more control over map styles, integration of diverse data sources, or advanced feature customization.
Factor 3 – Performance Concerns: You may occasionally encounter performance issues with Mapbox, such as slow loading times or occasional glitches. Competitors may provide better-optimized solutions with improved speed, reliability, and performance for specific applications.
Factor 4 – Feature Gaps: Mapbox may lack certain features such as advanced offline functionality, enhanced routing capabilities, or specialized features like indoor mapping. Alternatives can bridge these gaps by offering more altered solutions.
Factor 5 – Data Ownership and Privacy: Using Mapbox involves sharing data with a third-party provider, which might raise privacy concerns. Some alternatives prioritize data privacy, allowing users to retain more control over their data and comply with specific security requirements.
Factor 6 – Open-Source Preference: For developers favoring transparency and community-driven innovation, open-source mapping solutions like OpenStreetMap can be preferable. These alternatives enable greater control, collaboration, and cost savings.
Factor 7 – Vendor Lock-In: Relying solely on Mapbox can lead to vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility. Some alternatives provide greater freedom to switch providers or combine multiple mapping solutions to avoid dependency on a single platform.
Factor 8 – Industry-specific: Mapbox does not specialise in automotive navigation and logistics solutions, whereas HERE Technologies does. Radar excels in geofencing and location tracking while Mapbox does not.
Factor 9 – Core Mapping features: Some of the features offered by Mapbox’s alternatives but not Mapbox could be the availability of a rich Points of Interest (POI) database, including landmarks, businesses, and restaurants.
Key Features of Mapbox
With Mapbox’s accurate location data and adaptable developer tools, any company can incorporate geospatial elements into their apps and use location intelligence to improve operations. Some of the features of Mapbox are:
- Data Management: Manages geospatial data with powerful tools for uploading, processing, and hosting datasets and utilizes Mapbox Studio to manage and customize map data, including vector tiles and imagery.
- Data Visualization: Builds stunning, interactive maps to visualize complex datasets in real-time and creates heatmaps, choropleth maps, and 3D visualizations to extract insights from location-based data.
- Map Creation: Designs custom maps with Mapbox Studio, offering fine-grained control over style, colors, layers, and map elements. Integrates with web and mobile platforms using Mapbox GL JS and Maps SDKs for iOS and Android.
Pricing Information of Mapbox
With its range of APIs and SDKs, Mapbox provides a free tier for companies of all sizes to begin developing. The majority of Mapbox products include monthly pay-as-you-go prices that don’t include upfront licenses or contracts. All accounts also come with access to Mapbox Studio, a robust browser-based tool for managing data and styling maps.
- Mapbox GL JS for Web Maps: Pay-As-You-Go (per month). A map load occurs whenever a Map object is initialised. Unlimited interactivity with web maps.
- Maps SDKs for Mobile (iOS & Android): Pay-As-You-Go (per month). Based on monthly active users. You can make unlimited Vector Tiles API and Raster Tiles API requests.
- Navigation SDK: Pay-As-You-Go (per month). Metered Trips: Pay only for trips your users take. Unlimited Trips: Flat fee per user, regardless of usage.
- Mapbox Search (Geocoding): Pay-As-You-Go (per month).
- Temporary Geocoding API: Forward and reverse geocoding for dynamic searches.
- Permanent Geocoding API: Store results permanently, batch geocoding available.
- Temporary Geocoding API: Forward and reverse geocoding for dynamic searches.
- Mapbox Support Plans: Starting at: $50.00 per month. Guaranteed email response times. Guidance on API syntax and technical best practices. Premium plans customised for strategic partnerships.
Benefits of using Mapbox
Some of the benefits of Mapbox are:
- Customizable: Complete command over data integration and map design for unique experiences.
- Scalable: Made to manage applications with large traffic levels with dependability and performance.
- Interactive: Create captivating user experiences by creating dynamic, immersive maps.
- Real-Time Insights: Quickly update and present dynamic data with ease.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Easily distribute maps across iOS, Android, and the web.
Mapbox empowers businesses to create powerful, data-driven maps altered to their needs, offering flexibility, performance, and stunning visualizations.
Disadvantages of using Mapbox
Here are few of the disadvantages of using Mapbox:
- Mapping Issues: Some users have reported inconsistencies and inaccuracies in map data, which can affect user experience and application performance.
- Feature Limitations: While Mapbox offers a robust set of tools, it may lack certain advanced features that developers need, such as better offline capabilities or specialized mapping options.
- Inaccurate Geolocation: Occasional inaccuracies in geolocation services can lead to incorrect coordinates, impacting navigation and location-based applications.
- Learning Curve: Mapbox’s extensive customization options and APIs can be challenging for new users, requiring time and effort to master the platform.
- Learning Difficulty: Developers unfamiliar with mapping technologies may find the setup and integration of Mapbox more complex compared to simpler alternatives.
What are the Top 10 Mapbox Alternatives and Competitors in 2025?
The top 10 best Mapbox Alternatives and Competitors are:
- NextBillion.ai Maps
- Google Maps
- Azure Maps
- Here Maps
- Salesforce Maps
- Carto
- Esri ArcGIS
- OpenStreet Maps
- GeoServer
- Radar
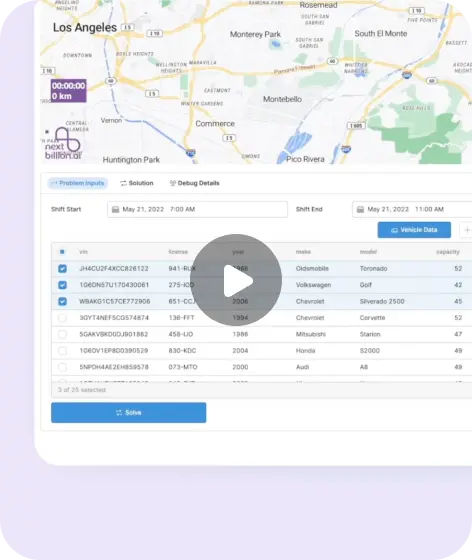
1. NextBillion.ai Maps
NextBillion.ai is a highly specialised platform focusing on custom mapping, geospatial data, and route optimization, perfect for companies that need flexibility and control over their geospatial assets.
Key Features
Primary Features
Primarily focuses on mapping, location intelligence, and geospatial data solutions. NextBillion.ai is particularly strong in route optimization, custom map-building, and AI-driven mapping services.
Routing and Optimization
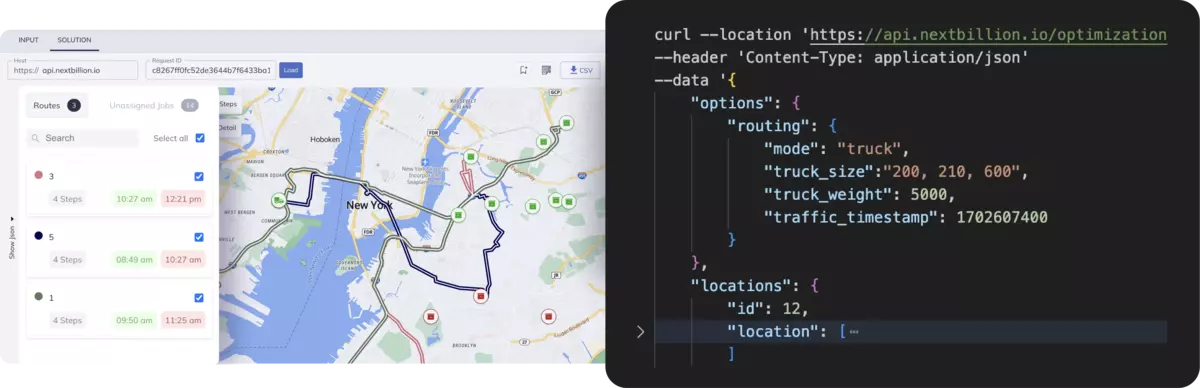
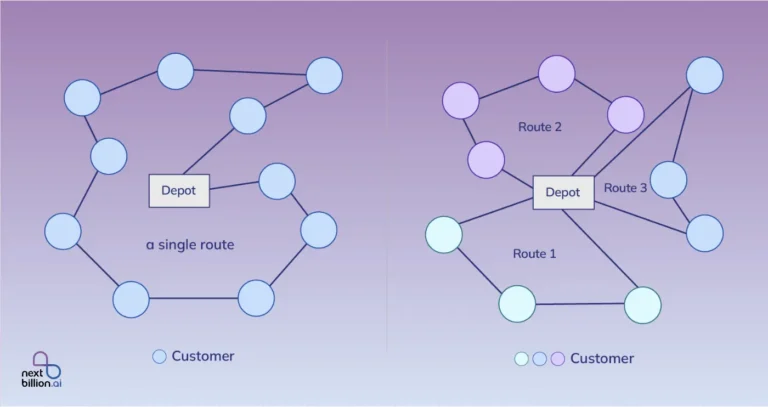
NextBillion.ai offers AI-driven route optimization for delivery and fleet management. NextBillion.ai provides APIs for precise route optimization tailored to different industries (for example, on-demand delivery, long-haul logistics).
Map Customization
NextBillion.ai enables businesses to customise maps according to their specific needs, such as defining geofences, altering map appearance, and integrating their own datasets. NextBillion.ai offers high flexibility for industries with unique mapping requirements (for example, logistics, e-commerce).
Geospatial Data and API Integration
NextBillion.ai provides a range of APIs for location data, map visualisation, and geocoding services. Supports custom geospatial datasets, which can be integrated into the platform to fine-tune routing and mapping solutions.
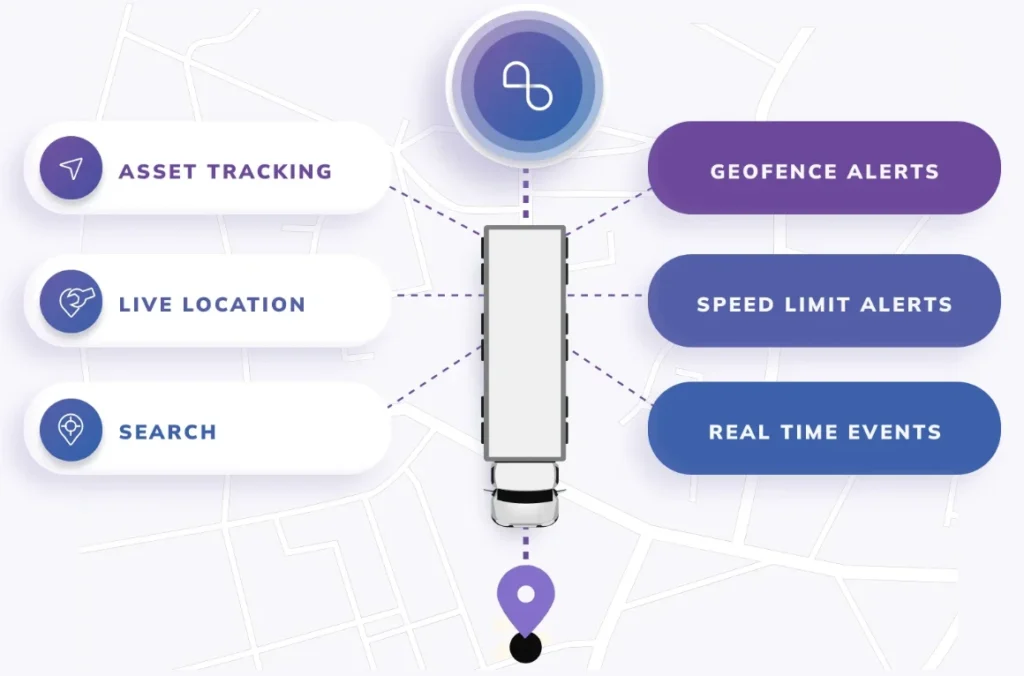
Real-Time Tracking and Visibility
NextBillion.ai offers APIs for real-time tracking of vehicles and assets, helping businesses track fleets and deliveries in real-time through customizable interfaces. Highly flexible in terms of how tracking data is presented or integrated with other platforms.
Analytics and Reporting
NextBillion.ai offers APIs for data collection, analytics, and reporting on location data, traffic patterns, and delivery efficiency. Custom reports can be generated based on geospatial data and fleet performance.
Pros and Cons
✅ Highly Customizable: NextBillion.ai provides a high degree of flexibility in customising routes based on business-specific requirements. This is beneficial for industries that have specific needs like ride-hailing or last-mile delivery.
✅ Industry-Specific Solutions: The platform excels in offering tailored solutions for specialised industries such as logistics, e-commerce, and ride-hailing, where real-time changes and specific geospatial requirements are essential.
✅ Real-Time Traffic and Historical Data: NextBillion.ai integrates real-time traffic and historical data, allowing businesses to optimise routes dynamically based on current conditions.
✅ Support for Poor Data Regions: NextBillion.ai is particularly strong in regions with limited or poor mapping data, enabling businesses to upload their own geospatial data for better route accuracy.
✅ Scalability: NextBillion.ai APIs are highly scalable, making it suitable for both small and large businesses with different route optimization needs.
❌ The high degree of customization requires a more complex integration process, making it potentially harder to adopt without technical expertise.
❌ While NextBillion.ai excels in specific regions with limited data, it might not have the same level of global coverage or deep data integration that some larger players in the market offer.
Reviews
- “Good experience with Mapping APIs” – Accuracy and Customer support along with affordability.
- “Seamless sales experience, everything working as expected” – It provided the same functionality as my previous provider at a lower cost
- “Location Tech APIs from Nextbillion.ai”- APIs are rich in features along with amazing customer support

Pricing
Custom Pricing: NextBillion.ai typically offers custom pricing plans based on the specific needs and scale of the business. While this can be cost-effective for large enterprises, it may be less accessible for smaller projects or businesses with limited budgets.
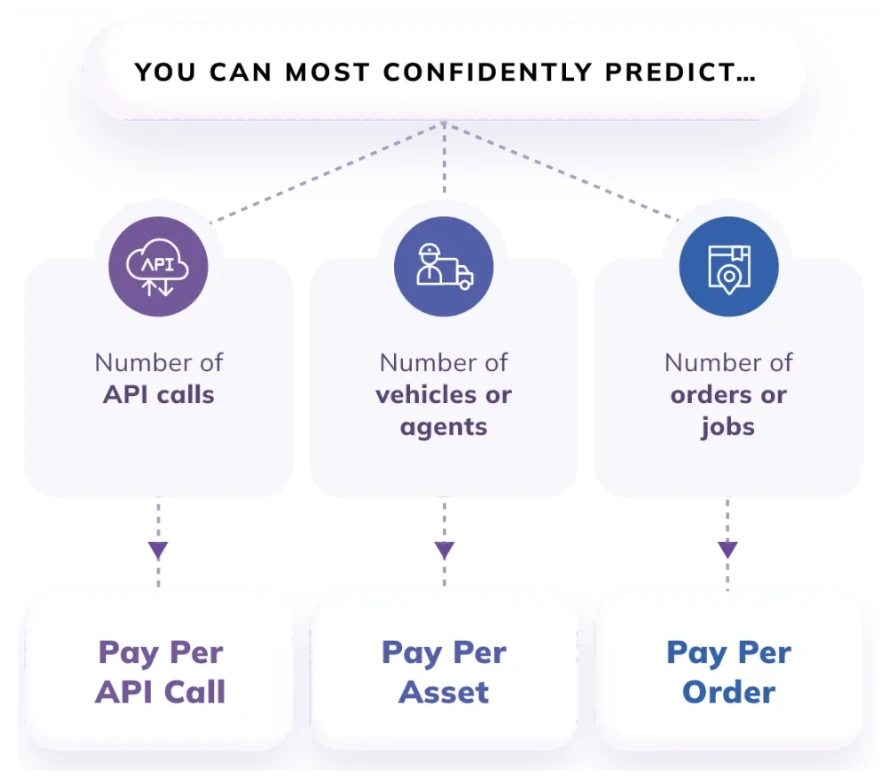
NextBillion.ai pricing is designed to align with the value you get. You can choose from three product bundles depending on your use cases and three pricing units – per-order, per-asset or per-API call depending on your business model. The per unit price is calculated based on your monthly usage volume and average order value (per unit cost goes lower as volumes increase and average order value decreases). A free trial of Nextbillion.ai is also available.
NextBillion.ai offers flexible pricing plans tailored to businesses’ diverse needs. Whether a company is an emerging startup or a large-scale enterprise, there’s a plan designed to optimise delivery operations efficiently.
- The Basic Plan is optimised for emerging and compact operations, including access to base APIs, support for only cars, and email support & community resources.
- The Advanced Plan offers enhanced features for growing businesses, including access to advanced APIs, support for trucks & motorcycles, and premium support.
- The Bespoke Plan provides comprehensive solutions for large-scale enterprises, including access to the enterprise product suite, support for all vehicle types, a dedicated solutions engineer, and white glove onboarding support.
2. Google Maps
The mapping platform Google Maps API offers Street View pictures, driving directions, and more.
Key Features
- Management of Data: Businesses and developers may easily manage their location-based data thanks to Google Maps’ effective processing of geospatial data:
- Data Capture: Makes it possible to collect real-time location data by integrating with GPS devices and APIs.
- Data Storage: Enables large-scale geospatial data storage by offering cloud-based storage choices via Google Cloud.
- Publishing: Using APIs and interactive SDKs, developers can include maps into internal tools, websites, and applications.
Pros and Cons
✅ Intuitive interface and seamless integration with multiple platforms make navigation simple for users of all skill levels.
✅ Provides highly accurate location tracking, essential for everyday navigation and business operations.
✅ Enables proximity searches for nearby restaurants, gas stations, or attractions
❌ Certain regions or rural areas may experience less precise location accuracy.
❌ Inconsistent data on distances, estimated travel times, or minor road networks.
Reviews

Pricing
Google Maps offers a $200 monthly free credit, which covers basic usage for most applications. Pricing beyond the free tier is based on specific API calls:
- Dynamic Maps: $7 per 1,000 requests.
- Directions API: $5 per 1,000 requests.
- Geocoding API: $5 per 1,000 requests.
- Places API: $32 per 1,000 requests for Autocomplete (session-based).
3. Azure Maps
With its robust geospatial features and abundance of new mapping data, Azure Maps offers developers across various industries the ability to give web and mobile apps a geographic context.
Key Features
A collection of web services called Azure Maps Traffic is intended to let developers build mobile and online applications based on real-time traffic data. Maps can be created using this data, or it can be utilized to create more intelligent routes that take into account the driving circumstances at the moment.
Coverage details for Azure Maps routing are given in this post. Azure Maps provides an ideal path from point A to point B in response to a search query.
Pros and Cons
✅ Azure Maps offers a user-friendly interface with intuitive APIs that integrate seamlessly into the Microsoft ecosystem. It is well-suited for developers familiar with Azure services, making implementation smoother.
✅ Robust location-based services such as geocoding, reverse geocoding, and spatial operations provide precise location insights.
✅ Advanced geolocation features, leveraging Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure, ensure precision and scalability. It is useful for real-time tracking applications and geospatial analytics.
❌ While accurate for many regions, there can be challenges in achieving the same precision in remote or underdeveloped areas.
❌ Certain regions might lack detailed maps or have inconsistencies in representation, limiting its usability in some areas.
Reviews

Pricing
Azure Maps follows a consumption-based model with pay-as-you-go pricing across its services:
- Render API: $4 per 1,000 transactions.
- Route API: $5 per 1,000 transactions.
- Geolocation API: $1 per 1,000 requests.
- Weather Service: $0.50 per 1,000 calls.
- Traffic API: $10 per 1,000 calls.
4. HERE Maps
The top-ranked platform for creating maps and providing location data services according to the Ovum Location Platform Index is HERE.
Routing and Fleet Management, Mapping, and Geocoding and Search tools are among HERE’s freemium offerings.
Key Features
- HERE Technologies offers a platform and services for developing location-aware applications that may be used for a variety of tasks, including routing, geofencing, logistics, fleet management, geocoordinate conversion into real addresses, and map display and customization.
- HERE Location Services: SAP API Business Hub, Microsoft Azure, MuleSoft, and AWS. HERE remains the leading location and mapping platform for Counterpoint Research.
- HERE maintains its lead over Google, taking the top spot in the Ovum Location Platform Index in 2019.
Pros and Cons
✅ Location-Based Services: HERE Maps is appropriate for use cases involving logistics and navigation since it provides strong location-based services including geocoding, reverse geocoding, and real-time traffic updates.
✅ Usability: Because of its thorough documentation and developer-friendly interface, the platform is comparatively simple for developers who are already aware with mapping APIs.
✅ Customer Service: In order to help developers and companies integrate and troubleshoot their services, HERE offers dependable customer assistance.
❌ Problems with the API: Some users complain that the APIs are occasionally unstable or have problems that impact how well their apps run.
❌ Learning Curve Difficulty: The platform’s initial setup and feature integration may be difficult for developers or beginners who are not familiar with mapping APIs.
Reviews

Pricing
- Freemium: $0/month: Build your app, service or web map for free, no credit card required. Transactions per month 250K, pay per additional Transactions 1000 / $1, SDK Monthly Active Users 5K and many more.
- Data Hub Add-on: $45/month. All of Freemium plus a little extra. Data transfer per month 10GB, database storage per month 10GB, pay per additional Data transfer 100MB / $0.45, and many more.
- Pro: $449/month. Boost your limits and add support. Transactions per month 1 Million, pay per additional Transactions 1000 / $1, SDK Monthly Active Users 5K, and many more.
5. Salesforce Maps
Use CRM-based sales mapping tools to sell more effectively. Use customer record visualization to make more informed prospecting selections. Automate record-keeping duties to save time, streamline account planning while in the field, and optimize field routes.
Key Features
- Cartography Map Design: Makes maps that are aesthetically pleasing and adaptable to your company’s requirements.
- Master Routing: Creates intricate, multi-stop itineraries to cut down on travel time and increase efficiency.
- Master Scheduling: Oversees extensive scheduling that takes into account numerous teams, cars, or projects.
Pros and Cons
✅ Features: Comprehensive features such as routing, scheduling, and analytics provide all-in-one solutions for location-based needs.
✅ Route Optimization: Enables efficient routing to save time and resources while improving overall operational efficiency.
✅ Map Creation: Easy-to-use tools for creating and customizing maps tailored to specific business requirements.
❌ Difficult Learning: The complexity of setup and advanced configurations can make initial onboarding daunting.
❌ Learning Difficulty: Requires significant training and familiarization, especially for non-technical users.
Reviews

6. Carto
As the top cloud-native location intelligence platform in the world, CARTO helps businesses employ spatial data and analysis for a variety of purposes, including more effective delivery routes, improved behavioral marketing, and well-placed stores. Leading companies like Coca-Cola, Vodafone, JLL, Deliveroo, and others trust CARTO. Using the capabilities of spatial data science, data scientists, developers, and analysts utilize CARTO to forecast future events and enhance business operations.
Key Features
- Predictive and Distance Analysis: Enables users to anticipate trends and outcomes by leveraging geospatial data, integrating machine learning models for advanced forecasting. Measures proximity or accessibility, essential for understanding coverage areas, nearest facilities, and travel times.
- Spatial Analysis: Provides tools for uncovering geographic patterns, clustering, and correlations to optimize decision-making.
- WYSIWYG Design: A “What You See Is What You Get” approach simplifies map and report creation, ensuring outputs match user intent.
Pros and Cons
✅ Carto delivers precise geospatial data integration, ensuring reliable insights and analysis across diverse use cases.
✅ The platform excels in cartography, offering polished and visually appealing maps, suitable for presentations and decision-making.
✅ Carto’s intuitive interface and streamlined tools make it accessible for users with varying levels of technical expertise.
❌ Despite its intuitive interface, some advanced features require a steep learning curve, particularly for users unfamiliar with geospatial analysis or coding.
❌ While generally supportive, there have been occasional reports of delayed responses or inconsistent assistance for certain technical issues.
Reviews

Pricing
- Enterprise – Small: Designed for smaller teams seeking advanced spatial analytics with basic enterprise capabilities. Free Trial is available. Includes features such as 3 Editors and 15 Viewers, 180,000 usage units per year, Cloud Deployment, SLA and usage metrics, 25 API Access Tokens.
- Enterprise – Medium: Ideal for cross-functional teams requiring analytics at scale with enterprise-grade support. Free Trial is available. Includes features such as 10 Editors and 50 Viewers, 600,000 usage units per year, Cloud Deployment, SLA, usage metrics, audit logs on-demand, and SSO, l100 API Access Tokens
- Enterprise – Strategic: A custom package designed for larger enterprises managing complex analytics across multiple teams. Features include unlimited Editors and Viewers, 3,000,000 usage units per year, Cloud and Self-Hosted Deployment, SLA, usage metrics, audit logs on-demand, SSO, groups, and custom branding, 30M geocoding, isolines, and routing operations annually.
7. Esri ArcGIS
ArcGIS is a full array of tools and features for mapping and location intelligence. ArcGIS can be installed locally (ArcGIS Pro), remotely or on-site (ArcGIS Enterprise), or as an Esri-hosted software as a service (ArcGIS Online). ArcGIS offers targeted applications to provide comprehensive solutions for your company or group.
Key Features
- Data Capture and Storage: Collect data from various sources, including GPS devices, satellite imagery, and field applications like ArcGIS Field Maps. Store geospatial data efficiently using enterprise geodatabases, cloud-based systems, or local storage solutions.
- Buffer Zone Query: Define areas around geographic features for proximity analysis, such as service areas or impact zones.
- Data Visualization: Transform raw data into engaging visuals like heatmaps, choropleths, and 3D representations.
Pros and Cons
✅ Seamlessly integrates with various data sources, third-party tools, and enterprise systems, ensuring compatibility with existing workflows.
✅ Offers robust and flexible tools for designing detailed and interactive maps, suitable for a variety of applications, from urban planning to environmental monitoring.
✅ Delivers advanced spatial analysis capabilities, enabling users to perform detailed and complex analyses such as predictive modeling and spatial statistics.
❌ The pricing structure can be prohibitive, particularly for organizations requiring multiple licenses or advanced features.
❌ Mastering ArcGIS can be challenging for new users, particularly when working with its advanced functionalities and tools.
Reviews

Pricing
- Subscription Plans: Pricing is per year, per user ($$$). Technical Support is included in the subscription. Service credits are used for specific cloud-based services such as geocoding, hosting feature or tile services, and spatial analysis. Credits are consumed as these services are utilized.
- Special Plans: Discounted plans are available for nonprofit organizations and NGOs. Customised plans for K-12, vocational schools, and higher education institutions. Affordable licensing options are available for non-commercial, personal use.
- E-Learning: Subscriptions include unlimited organization-wide access to Esri’s e-Learning platform.
8. OpenStreet Maps
OpenStreetMap (OSM) is the free editable map of the whole world.
Key Features
- Data Capture: Collects geospatial data through GPS devices, satellite imagery, aerial photography, and community contributions. Data is continuously updated by a global network of contributors.
- Data Visualization: Renders maps in various styles to highlight features such as roads, buildings, and natural landscapes. Supports visualization of complex datasets, enabling detailed analysis and representation.
- Overlaying: Combine multiple data layers to analyze spatial relationships, such as infrastructure and environmental features. Enables integration of custom data with OSM maps for personalized use cases.
Pros and Cons
✅ OpenStreetMap is user-friendly and accessible to a wide range of users, including beginners. Its simple interface and community-driven tools make mapping and data editing straightforward.
✅ OpenStreetMap delivers efficient and quick responses for tasks like geocoding, routing, and map rendering, making it suitable for real-time applications.
✅ OSM-powered tools support effective route optimization, enabling users to plan efficient paths for navigation and logistics purposes.
❌ Some regions may suffer from incomplete or inconsistent data due to reliance on volunteer contributions, leading to potential inaccuracies.
❌ Outdated Information: In rapidly changing areas, OSM data may lag behind, as updates depend on contributors’ efforts to keep information current.
Reviews

Pricing
- Free Access: OSM provides free access to its global map data, allowing users to download, modify, and share the data for both personal and commercial use. Contributions to OSM are voluntary, and the platform relies on donations to maintain its infrastructure.
- Third-Party Services: Many third-party providers use OSM data to offer value-added services such as geocoding, routing, and tile hosting. These providers charge based on their specific pricing models.
- Self-Hosting Costs: Organizations opting to self-host OSM data must consider infrastructure costs, including servers, storage, and maintenance. Costs vary depending on the scale of data usage and processing requirements.
9. GeoServer
GeoServer uses open standards to publish data from any significant spatial data source and is designed for interoperability. Web Feature Service (WFS), Web Map Service (WMS), and Web Coverage Service (WCS) are examples of industry-standard OGC protocols that are implemented by GeoServer. Extensions such as Web Processing Service (WPS) and Web Map Tile Service (WMTS) offer additional formats and publication choices.
Key Features
- Data Capture: Supports integration with a variety of data sources, including shapefiles, PostGIS, GeoJSON, and web services. Enables importing geospatial datasets directly for visualization and processing.
- Data Manipulation: Allows users to edit and process spatial data, enabling transformations, re-projections, and format conversions. Facilitates dynamic data updates with WFS-T (Web Feature Service – Transactional).
- Reporting: Generates detailed spatial analysis reports, integrating geospatial and attribute data. Offers tools for aggregating, querying, and analyzing data for decision-making.
Pros and Cons
✅ Supports almost all geospatial data format 3. Support all primary operating systems
✅ It is simple, OGC standard. It supports direct import of esri shape files. Cross platform support.
❌ It lacks support from the backend.
❌ Have issues when reprojecting into some co-ordinate reference systems.
Reviews

Pricing
GeoServer itself is free and open-source software, making it an attractive option for organizations looking to deploy a geospatial server without incurring licensing fees. Since GeoServer is based on open standards, it can be customized and extended to meet specific needs.
- Self-Hosting and Infrastructure Costs: Users need to account for the costs of hosting the server, including cloud or on-premises infrastructure, storage, and maintenance. Pricing for hosting GeoServer depends on the chosen hosting provider (e.g., AWS, Azure, or private servers) and the scale of the deployment.
- Third-Party Integration and Support: While GeoServer is free, third-party services or commercial support options may come at a cost. Some organizations opt for paid support from service providers to ensure system uptime, advanced troubleshooting, or custom development.
- Add-ons and Extensions: Some specialized plugins or extensions for GeoServer may incur additional costs, depending on the provider or customization needed.
10. Radar
Radar is the all-in-one location platform. Companies like Sleeper, Panera, DICK’s Sporting Goods, T-Mobile, and Zillow use Radar’s geofencing SDKs and map APIs to power location-based experiences across hundreds of millions of devices worldwide.
Key Features
- Radar helps you build amazing location-based app experiences.
- Radar is Privacy Shield-certified and GDPR-compliant.
Pros and Cons
✅ Integrations with client applications and customer data platform have been easy.
✅ The user interface is simple to navigate and for onboarding.
❌ Minimum radius to create fence and check the on change function.
Reviews

Pricing
- Free (Developers): 1,000 monthly tracked users, 100,000 monthly API requests, 1,000 geofences, and community support.
- Pay (Enterprise): Unlimited monthly tracked users, unlimited monthly API requests, unlimited geofences, dedicated support, unlimited accounts, multiple projects, premium integrations, user segments, trips dashboard, dedicated support, integration consulting, single sign-on and SLA available.
Why is NextBillion.ai the best alternative to Mapbox?
NextBillion.ai is a leading alternative to Mapbox by offering highly customizable mapping solutions designed to meet industry-specific demands in sectors like logistics, food delivery, and ride-hailing. With advanced route optimization, localized mapping expertise, and cost-efficient pricing, it is an ideal choice for enterprises looking for scalable and tailored solutions. Unlike Mapbox’s broader market focus, NextBillion.ai addresses challenges through simplified APIs and responsive customer support, enabling businesses to tackle unique operational constraints. Its commitment to enterprise customization and affordability makes it a top choice for organizations seeking precise, flexible, and dependable mapping tools.
Conclusion
Mapping platforms such as NextBillion.ai, Google Maps, Azure Maps, HERE Maps, Salesforce Maps, Cargo, OpenStreetMap (OSM), GeoServer, Radar, and Mapbox each bring unique strengths to the table, catering to diverse requirements. Google Maps is widely recognized for its vast global coverage and user-friendly APIs, making it ideal for consumer-facing applications, though its cost can be prohibitive at scale. Azure Maps shines in enterprise settings with seamless integration into Microsoft’s ecosystem. HERE Maps is a strong contender in the automotive and logistics sectors, offering advanced geolocation and navigation tools. Salesforce Maps focuses on CRM-driven geospatial insights, while Cargo excels in optimizing logistics and supply chain workflows. OpenStreetMap and GeoServer are favored for their open-source flexibility, offering cost-effective and customizable solutions. Radar specializes in location-based analytics for mobile and retail applications, while Mapbox is celebrated for its rich customization capabilities and exceptional dynamic visualization features, making it ideal for thematic maps.
Amid these comparisons, NextBillion.ai distinguishes itself as a standout alternative to Mapbox, especially for industries like logistics, ride-hailing, and e-commerce. With advanced route optimization, localized mapping expertise, and cost-effective pricing, it offers enterprises the scalability and flexibility they need. Its emphasis on solving industry-specific challenges, coupled with simplified APIs and responsive customer support, positions NextBillion.ai as a top choice for businesses seeking precise, customizable, and reliable mapping solutions.
FAQs
You can consider any of the other alternatives mentioned in this article, which best suits your business requirements. Apart from the ones mentioned in this article there are few others such as Tom Tom Map Maker, Map Tiler Cloud, and so on.
Mapbox: Primarily a mapping and visualization platform. It provides developers with APIs and SDKs to build highly customizable, interactive maps and location-based applications. It focuses on design flexibility and map customization.
Carto: Focuses on location intelligence and geospatial analytics. It is a platform for analyzing spatial data and creating insights, often used by data scientists, analysts, and businesses for decision-making.
Mapbox offers a free tier that includes up to 25,000 mobile users and 50,000 web map loads per month. Beyond this, the pricing starts at $5 per 1,000 loads for usage between 50,001 and 100,000, with rates decreasing as volume increases. In comparison, Google Maps is more costly, with Dynamic Maps priced at $7 per 1,000 requests.
About Author
Prabhavathi Madhusudan
Prabhavathi is a technical writer based in India. She has diverse experience in documentation, spanning more than 10 years with the ability to transform complex concepts into clear, concise, and user-friendly documentation.