Table of Contents
Shipping these days is becoming expensive day by day. There are many reasons that can be attributed to rise in shipping costs, starting from rising fuel costs to increased consumer demand but limited availability of shipping capacity.
From a logistics and transportation perspective, shipping costs can significantly impact the profit levels, and you can efficiently control the growing expenses by calculating cost per mile.
Cost per mile can be explained as cost of operating your fleet on a per-mile basis. This includes everything, including the cost of fuel, maintenance, insurnace, permits, driver’s salary and benefits, and administrative costs.
By calculating cost per mile, you can get a clear picture where your profits are draining, and once your know the gap, you will be able to figure out to fill up those gaps to achieve financial sustainability. You can break down the driving expenses into manageable chunks and optimize them efficiently.
Does Cost Per Mile Even Matter?
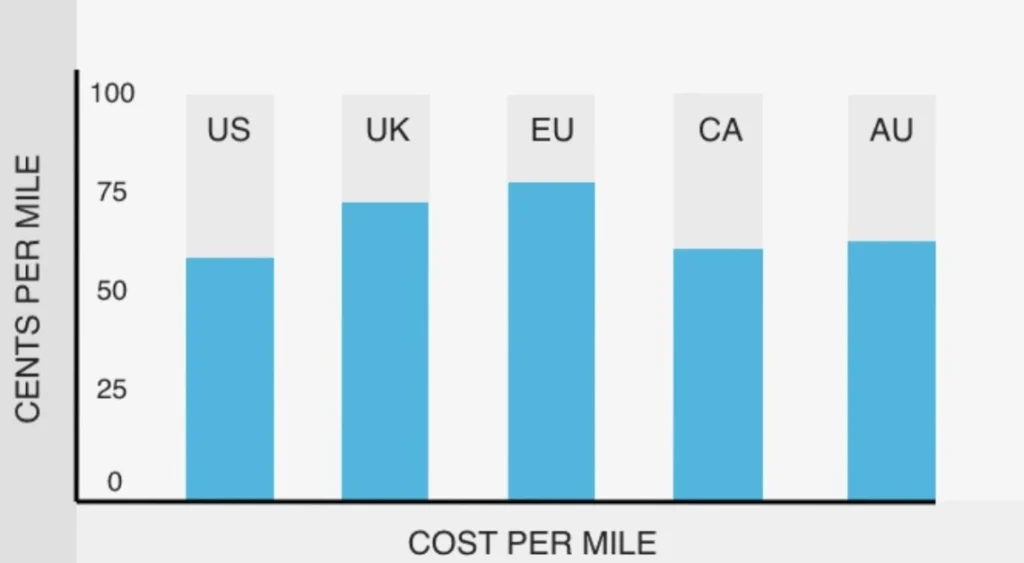
Yes, it definitely does. To understand this, you should look at the graph below, which represents the cost per mile of different regions.
According to this graph, the cost per mile in the United States is 58.5 cents per mile; in the United Kingdom it is 73 cents per mile; in the European Union it is 77 cents per mile; in Canada it is 59 cents per mile; and in Australia it is 60 cents per mile.
This makes the current average cost per mile for business use, which is 65.5 cents per mile.
Now, you might think that the value of cost per mile is insignificant since it is in cents, but when you add all the cents together, it makes a pretty substantial cost for businesses.
If you understand how you spend to drive each mile gives you detail on how much you need to earn to make a profit. Since, it is an essential expense, so you cannot cut it out, but you can definitely find ways to reduce the expenses and set rates accordingly.
Important Considerations For Calculating Cost Per Mile
It’s important to understand some factors that influence the value of cost per mile. These factors, which include your transportation cost in the calculation as well, help you decide the best price that is beneficial to your business as well as your customers. Here are three important things to consider:
1. Fixed Expenses
Understanding your business’s fixed costs is essential to calculating your cost per mile. These are usually the ongoing expenses related to your business that are rarely going to change. Insurance premiums, office space rent, and employee salaries are a few examples. These operating costs can add up quickly when using self-delivery services like trucks or other assets that also have depreciation costs.
2. Variable Expenses
Variable expenses are the dynamic business costs that var or change on a monthly basis. Hourly pay for staff members and office space utilities are two examples. Although there might be some monthly similarities, these expenses won’t be the same. As a result, you will have to set up and run your own tracking system for these costs.
3. Miles Driven
Similar to the two different types of mileage costs when figuring out the cost per mile, there are two different kinds of miles. It is imperative to track both compensated and deadhead miles or use a vehicle tracking system to manage this task. The distance traveled while actively en route to complete delivery is referred to as compensated mileage. Deadhead mileage, on the other hand, is the distance driven with the car empty following successful delivery.
Cost Per Mile Formula
The following cost-per-mile formula must be used to determine the cost per mile.
Cost Per Mile = Overall Delivery Expenses/Total Mileage
To put it simply, you need to divide the total logistics costs by the total miles traveled over the course of the trip.
Let’s take an example where your monthly expenses for last-mile delivery come to $5,000. The combined mileage of your vehicle is 2,000 miles. Thus, the following would be the cost per mile:
$5,000 / 2,000 miles = $2.50 per mile
This indicates that the average cost to complete a mile in your delivery process is $2.50.
Remember that this is only a simple calculation. It might not take into account all the particulars and details of your last-mile delivery operations. Consider any additional transportation costs that arise during home delivery.
How to Calculate Cost Per Mile? 4 Easy Steps
Let’s look at the calculation of calculating your cost with each mile traveled more comprehensively. Here are the following 4 simple steps to calculate cost per mile effectively:
Step 1. Determine Your Fixed Costs
To determine your cost per mile, begin by adding a column to your trucking expenses spreadsheet that contains all of your fixed costs. No matter how far you drive or how much goods you haul, fixed costs are expenses that stay the same from month-to- month.
If you pay the same expenses every year, divide the overall amount by 12 and add it to every month’s fixed cost total.
Step 2. Determine Your Variable Costs.
Next, include a column for variable costs in your spreadsheet. Expenses that vary every month based on how many orders you had to fulfill, how long your vehicles were used, as well as how many loads you haul carried out are known as variable costs. Depending on how much you use your vehicle, variable costs may change. These expenses are:
- Fuel: Your fuel cost will vary depending on how many miles you cover in a month.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Unexpected repairs and routine maintenance costs can change every month.
- Tolls and parking: Charges that change based on your driving patterns and routes.
You don’t need to divide any numbers by 12 since it wouldn’t make sense for any of your variable costs to be annual expenses. For example, your monthly variable costs come to $8000 when you spend $5000 on fuel, $2000 on monthly maintenance, and $1000 on tolls.
Step 3. Determine How Many Miles You Drove
You also need to calculate the exact number of miles you drove in the past month. Both compensated and uncompensated (also known as deadhead) miles should be included in your total mileage. In this instance, let’s assume that you traveled 10,000 miles in total last month. The example spreadsheet will look as follows:
Fixed Costs:
Fixed costs | Monthly amount |
Truck payment | $4,980 |
Insurance total (occupational accident insurance + unladen/non-trucking bobtail insurance + physical damage insurance + etc.) | $690 |
License plates (and IRP certification) | $154 |
Permits (things like a pre-pass) | $25 |
Total fixed costs (Adding all the costs) | $5,849 |
Total miles driven | 10,000 |
Variable Costs:
Variable costs | Monthly amount |
Fuel | $2,908 |
Food | $350 |
Freight costs (freight broker, dispatching service, load board fees, etc.) | $2,000 |
Semi-truck maintenance (repairs, tyres, etc.) | $628 |
Any other miscellaneous expenses | $200 |
Total variable costs (Adding all the costs) | $6,086 |
Total miles driven | 10,000 |
Step 4. How To Calculate Cost Per Mile
Once you have all the information, you can figure out your cost per mile. Divide your total miles driven by the sum of your variable and fixed costs to arrive at this amount.
Cost Per Mile = Total Miles/ (Fixed Costs + Variable Costs)
The example spreadsheet should now appear as follows:
Fixed Costs:
Fixed cost | Monthly amount |
Truck payment | $4,980 |
Insurance total (occupational accident insurance + unladen/non-trucking bobtail insurance + physical damage insurance + etc.) | $690 |
License plates (and IRP certification) | $154 |
Permits (things like a pre-pass) | $25 |
Total fixed costs | $5,849 |
Total miles driven | 10,000 |
Fixed Costs Per Mile | $0.59 = ($5,849/10,000 miles) |
Variable Costs:
Variable costs | Monthly amount |
Fuel | $2,908 |
Food | $350 |
Freight costs (freight broker, dispatching service, load board fees, etc.) | $2,000 |
Truck maintenance (repairs, tyres, etc.) | $628 |
Any other miscellaneous expenses | $200 |
Total variable costs | $6,086 |
Total miles driven | 10,000 |
Variable costs per mile | $0.61 = ($6,086/10,000) |
You can now calculate your total cost per mile by adding your fixed and variable costs per mile:
Fixed Costs Per Mile | $0.59 |
Variable Costs Per Mile | $0.61 |
Total Cost Per Mile | $1.20 |
Why Understanding Cost Per Mile is Important?
Businesses need to understand shipping costs per mile to make well-informed decisions regarding their logistics and transportation operations. You can benefit from accurate cost-per-mile calculations in the following ways:
- Analyze the profitability of specific clients or routes: You can determine which customers or routes generate higher profits by understanding fleet cost analysis. You can use this data to focus your resources more on those areas.
- Make data-driven pricing and contract decisions: Businesses can price their services and negotiate contracts with clients more effectively to reflect the service’s true cost by knowing their cost per mile.
- Determine cost-saving opportunities: By examining the different factors that affect the cost per mile, businesses can find cost-saving opportunities and implement efficiency-boosting strategies.
- Monitor the business’ financial health: The cost per mile can be used as a key performance indicator for tracking a company’s financial health, enabling managers and owners to monitor their progress over time.
How To Reduce Last Mileage Delivery Costs?
Once you learn your cost per mileage, you can think of the best strategies for reducing costs and speeding up delivery. These steps will also provide added benefits to your business. Some of these cost-saving measures are:
- Route planning: By using navigation apps, drivers can take the quickest or shortest routes to reach the destination. Additionally, traffic can be avoided along with reduced fuel consumption. Route planning is helpful in discovering unexplored and unknown roads.
- Optimize vehicle load: Increasing the load capacity of shipping vehicles will improve the effectiveness of your logistics. When items are divided evenly across trucks, fewer trips are made, resulting in lower gas costs and unlocking fleet efficiency.
- Monitor driver behavior: You can track driver behavior with telematics and tools (such as delivery driver applications) to monitor things like planned and actual mileage, speeding, idling, and forceful braking. You can train the drivers to promote safer and more fuel-efficient consumption driving. As a result, delivery drivers will use less fuel as a result and the repair expenses will also go down.
- Optimize inventory management: Invest in effective inventory management tools to avoid overstocking and save storage costs. This reduces the need for expensive fast delivery or additional trips by ensuring the right goods are delivered at the right times.
How NextBillion Can Help Minimize Drive Time And Save On Fuel?
Evolving technology can help you in understanding your cost per mile and NextBillion helps you utilize robust and reliable APIs and SDKs, so you can save on fuel and bring the cost per mile expenses into control. We offer route optimization API that will reduce the daily operational costs, boost customer satisfaction, and improve your delivery capacity.
This API will help you create dispatch-ready routes within seconds with 50+ constraints that will require no editing or on-road improvisations. You can easily add refueling stops or tools pickup stops to make the routes more logical and efficient, aligned to real-life scenarios. Moreover, you can even add new stops or service requests into ongoing routes with minimal changes to the existing routes.
Whether you focus on last mile approach or middle mile approach, this API is designed to lower the cost per mile.
NextBillion.ai, as your holistic tech partner, also offers APIs and SDKs to integrate Live Tracking feature which allows you to track your assets in real-life to an accuracy of upto 1 meter. You can even set up alerts and notifications for different triggers, like speeding, excessive idling, and others.
FAQs
Divide your entire monthly spending by the total number of miles you drove in order to get your cost per mile. For instance, your cost per mile would be $0.30 if you drove 10,000 miles and your expenses came to $3,000.
You have to divide the journey’s cost by the total distance traveled in order to determine your cost per kilometer. Divide the price by the entire distance in kilometers to find the cost per kilometer.
You can calculate the cost per mile using the following formula:
Cost Per Mile (CPM) = Total Delivery Expenses/Total Mileage
About Author
Joseph Jacob
Joseph Jacob is a seasoned author with over 7 years of business writing experience behind him. After graduating as an aerospace engineer, he briefly dipped his toes into the world of sports journalism before finding his vocation in B2B SaaS content writing.