

- BLOG
Smart Route Optimization for Alcohol & Beverage Distributors
Published: November 11, 2025
Route Optimization API
Optimize routing, task allocation and dispatch
Distance Matrix API
Calculate accurate ETAs, distances and directions
Directions API
Compute routes between two locations
Driver Assignment API
Assign the best driver for every order
Route Optimization Software
Plan optimized routes with 50+ Constraints
Product Demos
See NextBillion.ai APIs & SDKs In action
AI Route Optimization
Learns from Your Fleet’s Past Performance
Platform Overview
Learn about how Nextbillion.ai's platform is designed
Road Editor App
Private Routing Preferences For Custom Routing
On-Premise Deployments
Take Full Control of Your Maps and Routing
Table of Contents

Ever wondered how your favorite craft beer or fine wine arrives perfectly chilled and right on time, despite complex delivery routes and tight schedules? For alcohol and beverage distributors, that’s no accident, as it’s the power of smart route optimization in action. In a world where efficiency is the key to profit and customer satisfaction, intelligent routing technology turns logistics from guesswork into a science of precision.
Wonder how it works and how it will help you take your distribution game to the next level? Continue reading to see what the future of smarter and faster delivery of beverages holds
Research has found that optimized routing can reduce travel distance by around 10 percent, fuel consumption by 11 percent, and significantly cut related emissions.
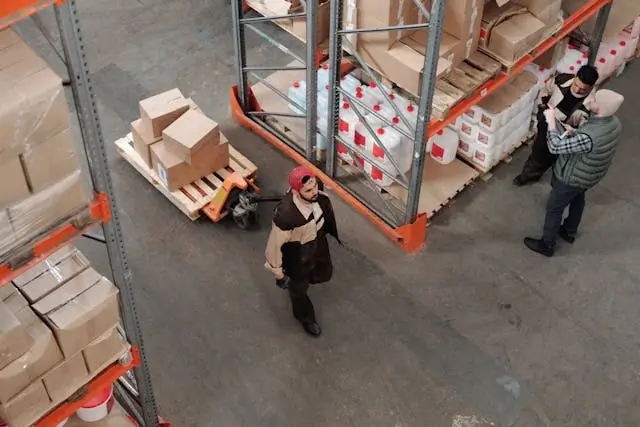
Fleet operations and fuel in beverage distribution constitute a significant portion of the total operating costs, normally 10-20% of the overall revenue of a company. These expenses are a heavy liability to an industry that has such narrow profit margins.
This is where optimized route optimization comes into play. With the help of data-driven algorithms, AI, and real-time visibility, distributors are able to minimize mileage, reduce idle time, and enhance service-level compliance.
Alcohol distributors work with on-premise (bars, restaurants, hotels) and off-premise (retail, supermarkets, convenience stores) accounts. The segments have different delivery windows, order frequencies, and service-level expectations. Solid route optimization allows dynamic scheduling and adaptive routing to react to such variables to avoid delays during delivery and minimize service disruption.
Distributors deal with thousands of SKUs: glass bottles as delicate as they are and kegs as massive as they are. The dimensional and weight characteristics of each type of product are unique, and load optimization is complicated. An efficient routing and load-planning system takes into account vehicle capacity, product fragility, stacking capacity, and delivery sequence to ensure the optimum use of the payload without compromising the integrity of the products and regulations.
Alcohol distribution is based on multi-jurisdictional restrictions such as limited delivery time, proof of age, and dry-zone regulations. In current route-optimization systems, geofencing and rule-based limitations are integrated to make sure that each stop meets local, state, and federal guidelines, automatically avoiding bans and restricted hours.
Peaks during holidays, festivals, and sporting events make route planning volatile. Smart route-optimization systems combine the use of previous demand forecasting and real-time sales information to dynamically increase or decrease fleet capacity and re-plan delivery routes, ensuring the reliability of service and reducing expensive overtime or stockouts.
Deliveries in the city center present logistical challenges in the form of restricted access areas, congestion fees, parking restrictions, and narrow streets. With the help of micro-routing algorithms and last-mile optimization, distributors can create efficient urban delivery loops that have low dwell time and adherence to municipal delivery windows.
High-quality drinks usually demand logistics that are temperature controlled. Optimized routing minimizes idle time, detours, and loading delays, safeguards product quality, and minimizes the energy consumption of refrigeration units, which are essential in preserving brand image and adherence to safety regulations.
Kegs, crates, and returnable bottles are often involved in alcohol distribution. Incorporation of reverse logistics in the same route plan enables drivers to efficiently make pickups on outbound routes, thus lowering total mileage, turnaround time, and environmental footprint.

Here are most prominent key logistics strategies for alcohol distributors that can help them achieve their goals:
Conventional fixed routes are predictable but not flexible. Contemporary distributors have embraced dynamic routing, whereby real-time inputs are utilized (traffic data, order volumes, and customer priorities) to calculate the most efficient daily routes. Several companies adopt the crawl-walk-run model of adoption, with the initial stage of partial automation (crawl), gradual integration of live data (walk), and finally full adaptive, AI-based routing (run).
Telematics offers live tracking of location, driver behavior analytics, and exception alerts. This allows dispatchers to track compliance, proactively reroute drivers, and provide real-time ETAs to customers. It converts a reactive dispatch model into a predictive, performance-oriented system, enhancing reliability and customer satisfaction.
Optimal fleet deployment refers to balancing the type of vehicle, load capacity, and route demand. With AI-assisted load optimization, distributors are able to calculate case weights, delivery volumes, and truck sizes to optimize legal payloads and reduce empty miles, increasing sustainability and profit margins.
Key accounts can have time slots that are not negotiable. High-end routing programs treat these as fixed constraints in the algorithm and optimize the rest of the deliveries around them, balancing the quality of service and the efficiency of the route without affecting the satisfaction of premium clients.
The division of areas into rational delivery zones will guarantee the density and efficiency of routes. By placing all drivers in small, close areas, there is less backtracking and less idle time, leading to lower fuel consumption, better predictability, and a greater number of deliveries per mile driven.
Fixed routing models cannot withstand volume pressure during peak demand seasons. Adaptive route optimization systems are dynamic, as they redistribute resources, reassign zones, and deploy standby fleets. Predictive analytics allow distributors to model delivery scenarios, balance workloads, and ensure on-time performance even at the highest peaks in demand.
Having strict delivery timelines, unstable demand rates of customers, and unpredictable fuel prices, AI-based route optimization and predictive analytics transform beverage logistics. Such systems do not just operate on a reactive planning style; they have evolved to predict and reduce disruptions before they happen.
Current smart systems amalgamated with the power of AI and predictive analytics combine real-time telematics, traffic information, order history, weather conditions, and even sporting or social event schedules so that the distributor can predict demand and program the most effective delivery routes before the first truck has left the depot.
AI predictive models are fed with several years of past sales data, marketing and promotion schedules, and external event notifications like holidays, concerts, or local festivals. When these data streams are correlated, the system detects demand spikes of specific SKUs or product groups in terms of time and place. This allows proactive planning, which is to reserve more fleet capacity, inventory in satellite depots, and reassign drivers long before order volume peaks. Predictive demand modeling converts the logistics of the peak period from a scramble or crisis into an operation that is based on data and preemptive.
Machine learning software processes drop density, stop proximity, frequency of customer orders, traffic congestion, and driver performance data to constantly optimize delivery zones and cluster routes.
This forms dynamically optimized territories, which change with a changing customer base or city infrastructure. Consequently, distributors experience equal distribution of workload, less overlap on routes, and quantifiable year-round improvements in fuel efficiency, on-time performance, and driver productivity.
AI-based dispatch systems combine GPS, telematics, and Internet of Things sensor feeds to automatically identify disruptions, e.g., road closures, vehicle failures, or order additions, and reread routes in real time.
The platform applies reinforcement learning and shortest-path algorithms in order to produce alternative paths in several seconds, maintaining delivery margins and customer SLAs without the use of manual dispatchers. Re-optimization ensures that there is zero downtime even in unstable delivery conditions.
ML models are advanced, which means that they take order data, packaging formats (kegs, bottles, cases), pallet structures, and vehicle specifications to determine the most appropriate structure of the load per route.
The system can simulate various load scenarios and thus will guarantee maximum load capacity without violating axle weight limits, stacking constraints, and refrigeration needs. The outcome is a reduction in the number of trips, fuel use, and CO2 emissions, which is accomplished through accuracy-based capacity planning.
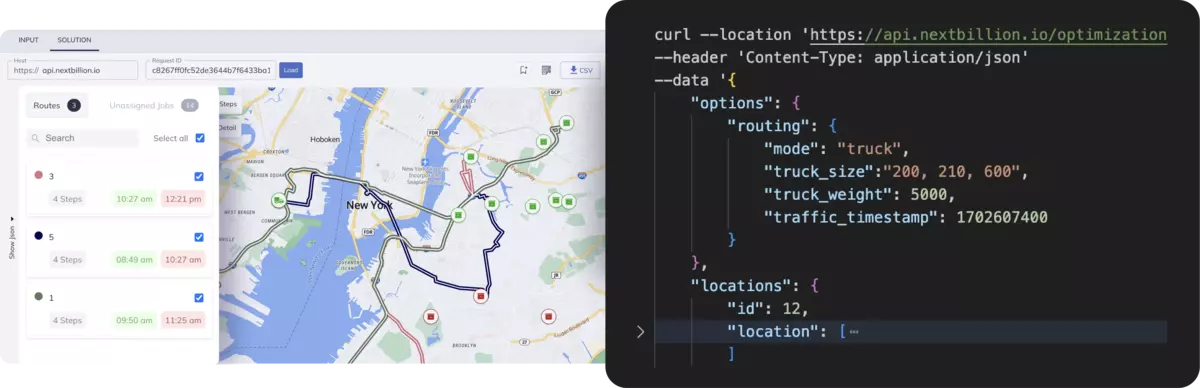
In the modern fast-paced alcohol and beverage distribution business, manual spreadsheets, fixed route maps, or older TMS modules are no longer able to keep pace with the dynamism required by the business. Route optimization software is an AI-based technology that combines predictive analytics, automation, and real-time adjustments to provide the next generation of logistics intelligence.
When companies deploy AI-based routing at scale, its potential impact becomes transformative, and this is where NextBillion.ai plays a pivotal role. In contrast to generic mapping solutions, NextBillion.ai offers enterprise-level, dynamic routing infrastructure that is specifically created to address the difficult operational issues of alcohol and beverage distributors.
Fundamentally, the system provides a powerful, AI-based Route Optimization API, which allows accurate and constraint-based planning and optimization of deliveries.

The software facilitates the specification of task-specific time windows, vehicle shift timetables, as well as driver skill parameters to fulfill compliance and service-level agreements.
The Route Optimization Flexible API of NextBillion.ai automatically allocates the routes and still complies with these operational limitations.
It shows that time-window sensitivity has a direct effect on task sequencing and assignment in that it assists planners to determine when tasks are not assigned under conditions of constraint inability. Vehicle points can also be started and ended dynamically according to depot assignments.
Key task attributes include:
The API of NextBillion.ai enables users to specify maximum possible waiting time per stop as a hard constraint to the routing engine. This is essential in controlling the idle time of the drivers and ensuring that the services are aligned to the goals of the service.
Jobs and deliveries are set up with:
This feature will guarantee that the system will not cross non-negotiable business or regulatory boundaries and will maximize the productivity of the drivers.
The Custom Cost Matrix feature allows users to recreate the real-world operating economics into the routing algorithm. The custom travel costs between nodes (e.g., cost between A and B) enable businesses to model toll fees, congestion penalties, or fuel consumption patterns.
The API of NextBillion.ai combines these parameters, which are specified by users, with route planning to reduce the overall operational cost without compromising the service quality.
The Custom Objective feature also makes the process more flexible, and the user can optimize the goal to be more specific, e.g.:
These goals could be integrated with vehicle cost variables, time-window variables, or re-optimization variables, which would make them highly responsive to the real-world dynamics of delivery.
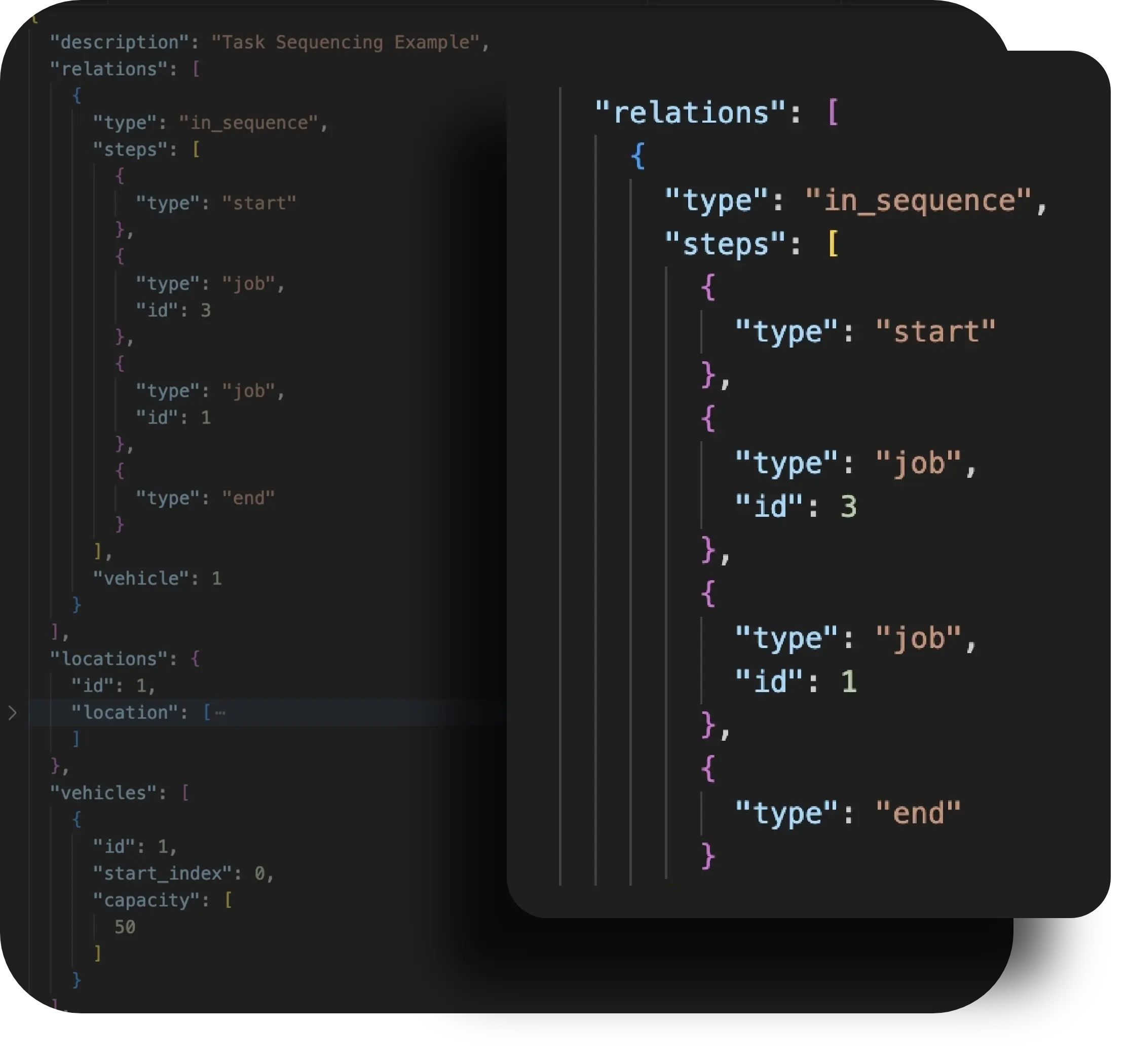
The API of NextBillion.ai can group orders, which is the option that enables the grouping of several nearby tasks into one stop within a specific radius. This drastically enhances the efficiency of drivers and lessens unnecessary parking or access attempts, particularly in large cities, residential communities, or shopping malls.
Task sequencing is also provided by the API using Relations, which are the manner in which jobs are carried out in a route. The following relations are supported:
These structures provide the ability to have dependent or sequence-sensitive deliveries, which are still subject to overall optimization logic.
Zone-based allocation provides administrators with the ability to limit or allocate vehicles to particular zones of service. These zones may be dynamically set up upon optimization or connected through Geofence API IDs. The functionality reduces overlap along routes, capitalizes on the familiarity of drivers with localities, and increases the density of delivery.
Route grouping also enriches the implementation of plans by minimizing overlaps of routes and unnecessary backtracking. It enhances the efficiency of routes, fleet, and service regularity, particularly when the volume of orders is high.
Being a good planner in beverage logistics requires spatial cognizance of cargo and vehicle capacity. The 3D capacity planning in NextBillion.ai takes volume, shape, and orientation factors into account instead of weight or quantity.
This allows loading of items based on their physical size, considering the capacity or inability of containers to be rotated or to be placed upright (e.g., kegs vs. bottles). In the case of alcohol distributors, such a model will avoid cargo misfit, product damage, and unused truck space, decreasing the number of vehicles needed and maximizing fuel efficiency.
The Soft Constraints module enables users to intelligently handle flexibilities that are related to time. It allows regulated slacking of delivery schedules or driver shift schedules within a pre-specified range.
This strategy is especially useful in situations where the rate of completion and customer satisfaction is more important than punctuality, e.g., in times of surge demand or unexpected interruptions. The system is able to achieve greater route completion rates with service reliability maintained by keeping an adaptive optimization logic.
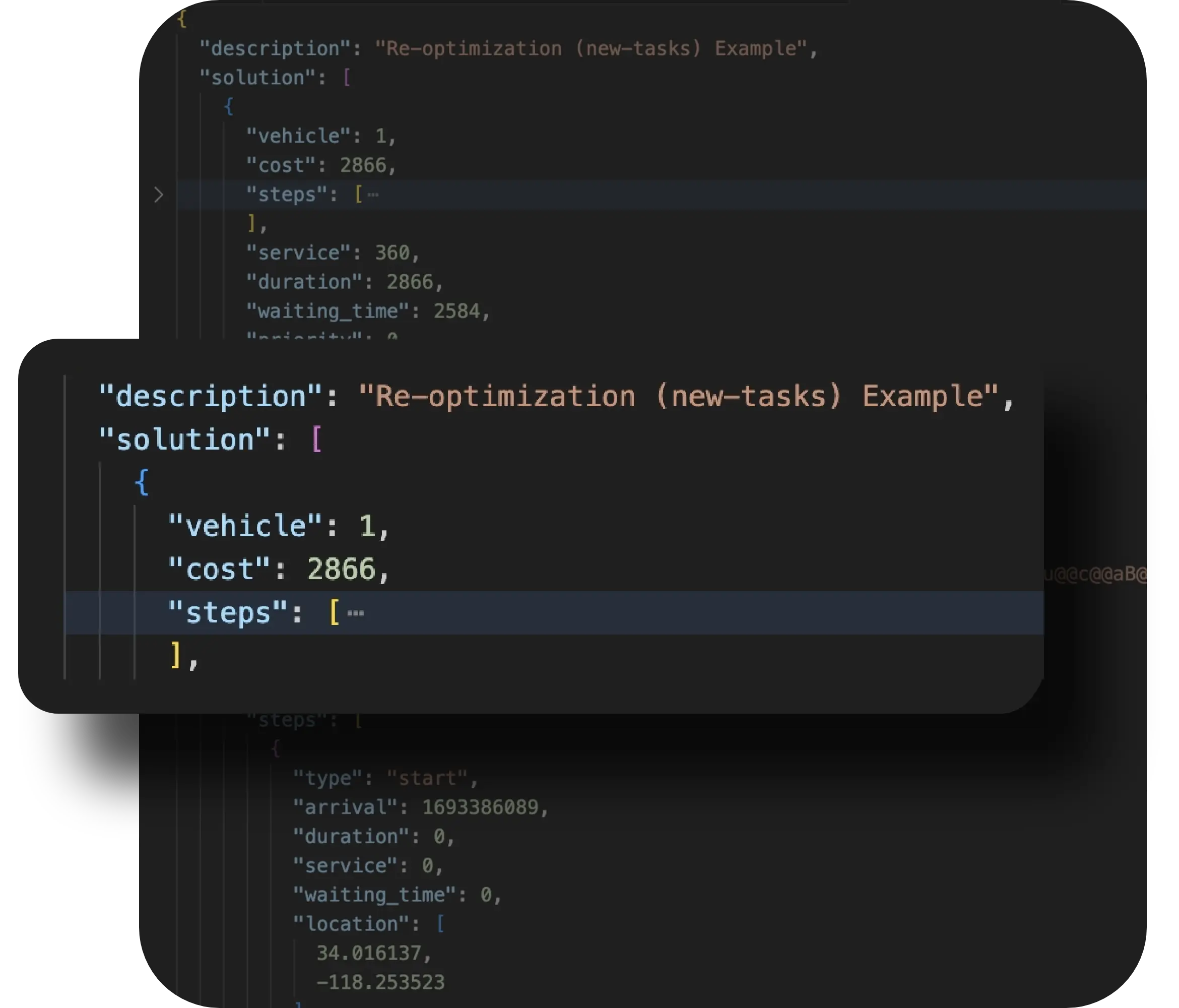
Empty miles, or the number of miles that a vehicle is on the road without a cargo, is a significant contributor to wasted fuel, capacity, and potential revenue in modern logistics and beverage distribution. They are often a result of poor route coordination, last minute cancellations, and inability to see the pickup opportunities nearby. NextBillion.ai deals with this issue using its AI-based Re-Optimization Engine, which is a feature that constantly re-optimizes delivery and pickup routes based on real-time operational information.
Routing plans in real-time logistics operations need to respond continuously to real-world variables that are volatile, like:
The Re-Optimization API lets users update the existing route plans in a streaming mode. It helps to do that with references to their original request IDs, to add small but accurate changes, such as new jobs, canceled jobs, or redistributed loads, without re-optimizing the whole optimization. This design removes the computational cost of complete re-executions, which is much better for response time, processing efficiency, and operational flexibility. In this way, dispatchers will be able to redistribute resources, combine compatible delivery and pickup routes, and significantly decrease empty mileage, and maintain driver continuity and route integrity.
Using the example of a Non-Emergency Medical Transportation (NEMT) operator who is in charge of three cars and has an itinerary of dialysis, therapy, and outpatient appointments on a day-to-day basis. The dispatcher creates an optimal route plan in the morning that consists of six patient pickups and drop-offs.
Later in the day:
The dispatcher would then have to perform this task manually, and clear off the canceled trips, restart the whole optimization, and allocate the assignments, which might upset the whole driver fleet, even those not involved in the new assignment.
Using the Re-Optimization Engine of NextBillion.ai, the system does not change the structure of the existing plan, but adds localized changes: canceled pickups are removed, new high-priority stops are added, and only the parts of the plan that have changed are recalculated. This enables the dispatcher to ensure consistency of route, familiarity of the driver, and real-time responsiveness, which reduces idle mileage and maximizes capacity utilization, without human intervention.
Predictive backhaul planning can also be performed with AI-driven routing, which consists of finding profitable return loads to remove empty return trips. The algorithms of NextBillion.ai compute the historical delivery data, depot locations, vehicle telemetry, and the current order inflow to automatically pair the delivery endpoints with the closest pickup opportunities.
To beverage distributors, this implies:
Through the integration of forward and reverse logistics in one optimized cycle, distributors will be able to reduce empty mileage by a greater percent. They can further decrease emissions and increase the overall fleet utilization rates.
The NextBillion.ai platform can also be connected with ERP and WMS systems, so that the changes in the routes are aligned with the availability of inventory, the patterns of the customer orders, and the forecasts of the stock levels. This integration avoids unnecessary vehicle movements due to stockouts or partial loads, and it facilitates just-in-time replenishment, which is essential in the alcohol and beverage distribution networks dealing with perishable or regulated products.
Factor | Traditional Routing | Smart Route Optimization (AI-Driven) |
Routing Style | Manual, static routes. | AI-based, dynamic, real-time routing. |
Adaptability | Hard to adjust to changes. | Instantly re-optimizes for new orders or cancellations. |
Fuel & Fleet Efficiency | High fuel use, many empty miles. | Cuts fuel use by 15–25%, reduces empty trips. |
Delivery Scheduling | Fixed, inflexible windows. | Dynamic time-window and priority-based scheduling. |
Complex Deliveries | Struggles with mixed loads. | Optimizes 3D load, volume, and capacity planning. |
Compliance | Manual checks. | Auto geofencing and rule-based restrictions. |
Demand Forecasting | Reactive planning. | Predictive analytics for seasonal and event spikes. |
Visibility | Minimal tracking. | Real-time GPS, telematics, and ETA updates. |
Re-Routing | Requires full plan rebuild. | Partial re-optimization in seconds. |
Urban Deliveries | Inefficient in congested zones. | Micro-routing for last-mile efficiency. |
Backhauls | Empty return trips common. | Predictive backhaul management reduces waste. |
Scalability | Difficult to expand. | Cloud-based, multi-depot scalability. |
Cold Chain | Inconsistent temperature control. | Maintains product integrity with optimized routing. |
Sustainability | High CO₂ emissions. | Cuts emissions with efficient clustering. |
Integration | Limited system links. | Seamless ERP, WMS, and IoT integration. |
Outcome | Costly, rigid, low visibility. | Profitable, adaptive, and data-driven. |
In order to be competitive in the current logistics environment, beverage distributors must minimize empty miles and maximize on backhaul efficiency. The companies can turn the delivery operations into a nimble, data-driven ecosystem by applying AI-based route optimization, intelligent re-optimization, and predictive demand modeling. Suppliers who adopt the high-tech routing system like NextBillion.ai, simplify the fleet management, and optimize each mile travelled, will realize quantifiable benefits in cost-efficiency, sustainability, and customer satisfaction.
Schedule a demo and find out how the Route Optimization Software of NextBillion.ai can transform your alcohol distribution pipeline: less empty miles, more profitability, and smarter logistics performance.
Bhavisha Bhatia is a Computer Science graduate with a passion for writing technical blogs that make complex technical concepts engaging and easy to understand. She is intrigued by the technological developments shaping the course of the world and the beautiful nature around us.