Table of Contents
Imagine you’re late for a meeting in a bustling city, stuck in traffic, and unsure of the fastest way to get there. Or you’re a business owner managing a fleet of delivery vehicles, and every extra mile costs money. Whether you’re an individual user or an enterprise, navigation solutions are critical in saving time, reducing costs, and improving efficiency. Two of the most widely used navigation tools today are Waze and Google Maps, both owned by Google.
When it comes to navigation apps, Waze vs Google Maps is a debate that often leaves users divided. Both apps offer robust features for real-time navigation, traffic updates, and route planning, yet they cater to different user needs
Although both may seem similar initially, their purposes, features, and target audiences are vastly different.
While Waze thrives on community-driven updates that reroute drivers around obstacles, Google Maps is a versatile powerhouse that offers navigation, exploration, and business integration tools.
Yet, neither of these tools is a perfect fit for every scenario—especially for businesses managing complex logistics and delivery operations. This is where NextBillion.ai, a customizable geospatial solution, steps in.
In this blog, we’ll explore:
- What are Waze and Google Maps?
- Market Performance: How do they compare?
- Who are they built for?
- A detailed competitive analysis
- Limitations of Waze and Google Maps
- Why NextBillion.ai is an exceptional alternative
By the end, you’ll clearly understand the navigation landscape and why businesses should consider NextBillion.ai for enterprise-level solutions.

What Are Waze and Google Maps?
The Story of Waze
Waze was born out of a simple idea: leverage the power of community to make driving easier. Launched in Israel in 2008, Waze quickly gained popularity due to its real-time, crowd-sourced traffic updates. By turning drivers into active participants, Waze created a navigation experience that evolves as conditions change. Google acquired Waze in 2013 for $1.3 billion, incorporating its real-time data into Google Maps while maintaining Waze as a standalone product.
Google Maps: The Giant of Navigation
Google Maps, launched in 2005, has become the most comprehensive global mapping platform. From providing turn-by-turn navigation to offering satellite imagery, 360-degree street views, and detailed business information, Google Maps has become a household name. Its seamless integration with other Google services, such as Google Search and Google Assistant, makes it a versatile tool for many users.
Waze and Google Maps are renowned for their features, but they cater to different needs. Let’s take a deep dive into what makes each of these platforms unique and why they stand out in the navigation world.
Waze: The Social Navigator

Waze’s features revolve around crowd-sourced updates, leveraging its community to provide drivers with real-time insights. Its simplicity and focus on driving make it a favorite among commuters and delivery drivers. Below, we’ll explore these features in detail and their impact.
1. Real-Time, Crowd-Sourced Incident Reporting
At the heart of Waze lies its vibrant community of drivers. Every user acts as a sensor, reporting real-time incidents such as traffic jams, accidents, road closures, and hazards like debris on the road.
For example, imagine driving during rush hour in Los Angeles. A fellow driver ahead of you reports a minor collision on your intended route. Instantly, Waze flags the area as congested and suggests an alternative path.
The effectiveness of this system depends on user activity. Waze provides unparalleled accuracy in highlighting disruptions in areas with high user density.
2. Dynamic Routing with Constant Updates
Unlike traditional GPS systems, Waze is built to adapt. Its algorithms continuously process incoming data from users to identify faster routes and dynamically update your path.
Scenario: Suppose you’re delivering packages across a city. Midway through your route, Waze detects a construction zone, causing a significant delay. Within seconds, it recalculates your journey, saving you precious time.
This adaptability is particularly useful in urban areas with unpredictable traffic patterns.
3. Gamification: Driving Engagement
Waze has turned navigation into an engaging experience through gamification. Drivers earn points for reporting road incidents or updating map information. These points unlock ranks and badges, creating a sense of competition and camaraderie within the community.
For instance, you might see a “Waze Warrior” badge next to another driver’s icon, indicating their significant contributions.
This playful approach encourages user participation, which in turn enriches the platform’s data accuracy.
4. Integration with Location-Specific Advertising
Waze’s advertising model allows businesses to target drivers on their routes directly. For example, a nearby café can promote itself as a potential stop to users navigating in the area.
Ads are location-specific, meaning they pop up only when they are relevant to the driver’s current location. While this feature benefits businesses, it can occasionally disrupt the user experience.
5. Real-Time Fuel Prices
Waze provides a handy feature for cost-conscious drivers to compare fuel prices at nearby gas stations. Users themselves update this data, ensuring accuracy and helping drivers save money.
Example: As you’re low on fuel, Waze highlights the closest gas stations and their prices, letting you choose the most affordable option before refueling.
6. Voice Navigation with Custom Voices
Waze stands out with its customizable voice navigation feature. Users can record their voice prompts or choose fun, celebrity-inspired voices, making the navigation experience more personal and entertaining.
Imagine following directions narrated by your favorite celebrity or a loved one’s voice. It’s a small touch, but it adds a layer of charm to the app.
Google Maps: The All-Encompassing Navigator
Google Maps is far more than just a navigation app. Its comprehensive features make it an indispensable tool for many users, from travelers exploring new cities to businesses optimizing their logistics. Let’s explore the standout features that make Google Maps a global leader.
1. Multi-Modal Navigation
Google Maps supports various travel modes, including driving, walking, cycling, and public transit. It even combines these modes for seamless end-to-end navigation.
Scenario: A traveler in Tokyo might use Google Maps to find a subway route, then switch to walking directions for the last mile to their destination. This flexibility ensures users have an optimal plan for getting from point A to point B.
2. Offline Maps for Remote Areas
One of Google Maps’ standout features is the ability to download maps for offline use. This is especially useful in areas with limited internet connectivity, such as rural regions, or when traveling internationally without a data plan.
For instance, a hiker venturing into a remote mountain trail can download the area’s map in advance, ensuring they stay on track even without network coverage.
3. Extensive Business Listings and Reviews
Google Maps doubles as a local business directory, with millions of businesses listed alongside detailed reviews, photos, and operating hours.
Example: A user searching for “best coffee shops near me” can instantly see ratings, reviews, and even menu options, enabling informed decision-making.
This feature has made Google Maps a critical tool for businesses aiming to improve visibility and attract foot traffic.
4. Real-Time Traffic Monitoring
Google Maps combines sensor data and user reports to provide real-time traffic insights. Its heatmaps and color-coded routes make it easy to visualize congestion and plan accordingly.
Unlike Waze, which relies solely on user contributions, Google Maps supplements crowd-sourced data with extensive infrastructure and technology, enhancing accuracy even in areas with fewer active users.
5. “Explore” Feature for Discovery
Google Maps is more than a navigation app—it’s a discovery tool. The Explore tab offers personalized recommendations for restaurants, attractions, and events based on a user’s location and preferences.
Example: A tourist in Paris might receive suggestions for top-rated museums, charming cafés, and walking tours in their vicinity.
6. Google Street View and AR Navigation
Google’s extensive Street View feature allows users to explore streets and landmarks in 360-degree detail. It’s particularly useful for previewing destinations before visiting.
For urban explorers, Google Maps’ AR (Augmented Reality) navigation takes things further. By combining live camera views with directional overlays, users can navigate complex areas like busy intersections with ease.
7. Integration with Google Ecosystem
Google Maps seamlessly integrates with other Google products, such as Gmail, Calendar, and Photos.
Scenario: If you have a meeting scheduled in your Google Calendar, Maps can automatically notify you of the best time to leave based on current traffic conditions. This interconnected ecosystem adds convenience to daily life.
8. Detailed Public Transit Information
Google Maps excels in public transit navigation, offering schedules, real-time updates, and detailed routes.
For instance, a commuter in London can plan a journey involving the Tube, a bus, and a short walk, all within the same app.
Market Performance: How Do They Compare?
Waze: A Loyal Community
Waze’s 140 million active users may seem modest compared to Google Maps, but its niche focus ensures high engagement. Markets like the U.S., Brazil, and Israel see strong adoption, especially among drivers navigating urban congestion.
Google Maps: The Ubiquitous Leader
With over 1 billion monthly active users, Google Maps dominates the navigation space. Its global reach, expansive feature set, and integration with other Google products make it indispensable for personal and professional use alike.
Who Are They Built For?
Waze: Built for Drivers
- Primary Users: Commuters, taxi drivers, and delivery personnel.
- Strengths: Real-time updates, driver-focused routing, and location-based ads for small businesses.
Google Maps: Built for Everyone
- Primary Users: A diverse audience, including drivers, pedestrians, cyclists, and public transit users.
- Strengths: Comprehensive coverage, multi-modal options, and business integration.
A Side-by-Side Competitive Analysis
Feature | Waze | Google Maps |
User Focus | Drivers | General Users |
Real-Time Updates | Excellent – Community Driven | Good |
Offline Access | Limited | Comprehensive |
Interface | Fun and Engaging | Professional and Detailed |
Global Coverage | Limited | Extensive |
Business Tools | Limited (ads) | Comprehensive |
Multi-Modal Support | No | Yes |
Limitations of Waze and Google Maps
Waze
- Limited Appeal: Designed primarily for drivers, leaving out cyclists and public transit users.
- Data Reliability: Relies heavily on user reports, which may not always be accurate or timely.
- Global Reach: Coverage is less extensive in rural or less trafficked areas.
Google Maps
- Information Overload: This can overwhelm users with too many features and options.
- Privacy Concerns: Extensive data collection raises issues for privacy-conscious users.
- Ad Saturation: Businesses face stiff competition to stand out in crowded listings.
Enter NextBillion.ai: A Tailored Alternative
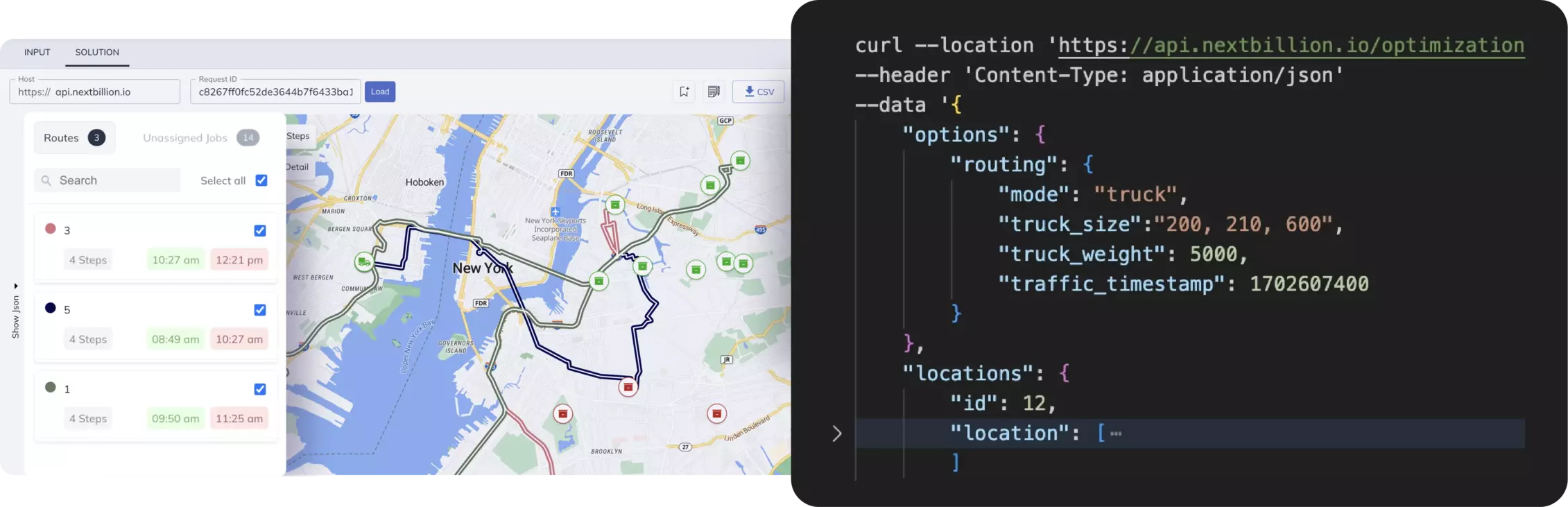
NextBillion.ai is a geospatial data platform that provides customized APIs for businesses. Unlike Waze and Google Maps, it focuses on delivering tailored solutions for enterprise clients, empowering them to address their unique navigation challenges.
Key Features of NextBillion.ai
- Customizable Maps
Businesses can design maps specific to their needs, from route optimization to last-mile delivery. - Scalable APIs
NextBillion.ai offers APIs for route planning, geofencing, and more optimized for industries like logistics and ride-hailing. - Privacy-Focused
With proprietary data controls, businesses can ensure data security and compliance. - Industry-Specific Solutions
Tailored for sectors such as retail, logistics, transportation, and urban planning.
Cost Efficiency
Offers flexible pricing, making it a cost-effective alternative to Google Maps API.
Real-World Applications of NextBillion.ai
Last-Mile Delivery

A logistics company can use NextBillion.ai to optimize delivery routes, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Fleet Management

Real-time tracking and geofencing ensure efficient operations for fleet managers.
Urban Mobility
Ride-hailing companies can customize routing algorithms for better driver-passenger matching and dynamic pricing.
Retail
Retailers can use geospatial insights to enhance location-based marketing and optimize store operations.
Why Choose NextBillion.ai?
- Custom Solutions: Unlike Google Maps or Waze, NextBillion.ai allows businesses to create solutions tailored to their needs.
- Cost-Effective: Avoid the high costs associated with Google Maps API while enjoying greater flexibility.
- Enhanced Privacy: Retain control over proprietary data, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
- Enterprise Focus: Explicitly built for businesses, offering better support and scalability.
Conclusion
While Waze and Google Maps are powerful navigation tools, they have their limitations—whether it’s Waze’s narrow focus on drivers or Google Maps’ overwhelming features and high API costs.
For businesses seeking a more tailored, cost-effective, and scalable solution, NextBillion.ai emerges as the ideal alternative. With its customizable APIs and enterprise-first approach, NextBillion.ai is not just a navigation tool but a strategic partner in achieving operational excellence.
Ready to transform your geospatial strategies? Explore NextBillion.ai today!
About Author
Rishabh Singh
Rishabh Singh is a Freelance Technical Writer at NextBillion.ai. He specializes in Programming, Data analytics and technical consulting, turning complex tech into clear and engaging content.