Table of Contents
Do you ship goods over long distances and are trying to find a cost-effective, efficient way? In that case, truckload shipping could be the best option for you. There are over 700,000 registered motor carriers, of which 91% operate six or fewer trucks and 97.3% operate fewer than twenty trucks, according to the US Department of Transportation.
With so many options available, businesses may find it overwhelming to choose the best freight solution. When we talk about transporting your freight with trucks, truckload is an essential term that you must be familiar with. In this guide, let us understand the truckload, its types, factors affecting the load pricing, and choosing your load partner.

Understanding the Concept of Truck Loads
A truckload is the quantity of goods that can be transported in a single vehicle. To put it simply, it refers to the amount of freight required to fill a trailer, which is typically greater than 10,000 pounds.
Freight is usually transported in trailers that are 48-53 feet long. These trailers can hold 45 pallets or up to 43,000 pounds of total goods.
Now, a question might arise: What is the standard used for defining a trailer as a truckload? The answer to that is: For a trailer to be considered a truckload, the freight must fill at least half of the trailer’s capacity and upto full capacity.
Shippers typically use the truckload method whenever they:
- Possess enough goods to fill a full truck
- Want the cargo to be in the trailer on its own
- The cargo is time-sensitive
- Determine whether it is more cost-effective than other methods
What Does Capacity Mean in Trucking?
The capacity of a truck-load truck refers to the total amount of space available for carrying loads. It provides valuable insights into supply chains and the potential impact of supply issues on the market. It can be divided into more specific types.
1. Seasonal Capacity
There are two main seasons in the trucking industry that impact capacity. In the first, most crops are harvested and need to be transported to markets during the produce season, taking place in April through July. Peak season is another important season to consider. This is the busiest time of year for manufacturers and retailers, running from August to October.
2. Regional Capacity
Not all parts of the nation are equally affected by the trucking industry’s seasonal effects, though. When it comes to available truckloads, some regions of the US are significantly busier than others. These are more popular among drivers because they make it easier to find loads as well as outbound loads to get home, also known as backloads.
However, in other regions of the nation, it is much harder to find a backload, which means fewer truck drivers are prepared to deliver. These areas are referred to as “black holes.” For instance, Dallas Seatle and Denver are the areas where manufacturing and distribution centers are low and consumption is high.
Therefore, at both the local and national levels, seasonal and regional factors can have a significant impact on trucking capacity and shipping rates. In order to ship loads from point A to point B, shippers and carriers must both be aware of how markets may change at any given time of the year.
Full Truckload (FTL) vs Less Than Truckload (LTL)
Two types of trucking operations are used to transport large volumes of freight: full truckload (FTL) and less than truckload (LTL).
FTL is generally from a single supplier and transported directly from a shipper to a consignee. The cost is usually on the cost per mile and changes daily, thus being more expensive. LTL shipments are less than 5000 pounds, which means they are smaller and require less space. These shipments cannot fill an entire trailer, so they require commercial vehicles. These vehicles carry goods from different locations of the businesses for shipment. They are cheaper than FTL; however, they are slower as multiple transfers require multiple stops.
Types of Truck Loads

Truckload freight can be classified into three main categories: dry vans, flatbeds, and refrigerated:
1. Dry Van Truckloads
A dry van is a type of semi-trailer truck with an enclosed interior to protect the cargo from the elements. Due to their design, these trailers are ideal for transporting loose cargo as well as cargo packed in boxes or on pallets. They provide affordability, good protection, and adaptability for the products they transport.
2. Flatbed Truckloads
Flatbed truckloads do not have physical walls surrounding the vehicle, giving transportation options greater flexibility. Loading cargo onto flatbed trucks is much simpler because they can be loaded from both the sides and the backside. For instance, for shipping forklifts or cranes, these can be used.
3. Refrigerated (Reefer) Truckloads
If certain temperature control is necessary for the shipment of goods, refrigerated truckload shipping is the best option. Fruits and vegetables, meats, and most other perishable products fall into this category. The unique high-powered vehicle can now control and preserve various temperature ranges, starting from 55 degrees Fahrenheit and reaching as low as -20.
Factors Affecting Truck Load Rates
Truckload rates are critical in the logistics industry, which is the core of global trade. The main factors that determine truckload rates and their effects on logistics procedures are given below.
1. Distance
The starting point is the distance between the source and the destination, which affects the base cost because of fuel usage, driver wages, and maintenance of the vehicle. Another significant factor influencing truckload rates is the distance along the chosen route between the cargo’s starting and destination points.
2. Weight or Volume
The operational costs of transporting goods are directly impacted by the weight or volume of the cargo being transported. Higher rates are necessary to cover the additional costs associated with carrying heavier loads, which also result in higher fuel consumption, increased vehicle wear and tear, and potential restrictions on the volume of cargo that can be transported in a single trip.
3. Supply and Demand Dynamics
The balance between supply and demand is the main determinant of truckload rates. The rates typically rise during periods of high demand, particularly during peak seasons like the holidays. Similarly, when supply decreases, prices can rise.
4. Fuel Prices
Fuel costs have a major impact on truckload operations costs. Its rates may directly rise in response to an increase in fuel prices. As a result, logistics companies need to monitor variations in fuel prices constantly.
5. Seasonal Effects
Truckload rates are based on seasonal variations, particularly when transporting cargoes that are dependent on the season, such as agricultural goods. Prices may rise during times such as harvest seasons when demand is higher.
How to Choose the Right Truck Load for Your Business?
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
To select the right truckload for your freight business, it is necessary to consider important things; these include calculating the freight volume and evaluating the best truckload load board or carrier:
Determining Freight Volume
A load’s cubic capacity, sometimes referred to as its volumetric weight, is an essential variable in both storage and transportation. By calculating this indicator, you can:
- Estimate a transport operation’s cost
- Maximize your space utilization
- Select the appropriate packaging for your transportation.
It can also be applied in several other cases. The following formula is typically used to determine a shipment’s volumetric weight:
LxWxH (in centimeters) / 5000
The cubic weight is a globally accepted standard indicator that reflects density, compares to actual weight, and provides an estimated value for the occupied space. Here’s how to measure:
Step 1: Measurement
Measure each item’s length, width, and height. The metric system is employed for this purpose since it is commonly accepted that the outcome should be expressed in centimeters.
Important tip: Figures always remain rounded up. If your product’s length is 144.5 cm, round up to 145 cm for the following calculations. Find out the specifications of the items contained in the package.
For example, you have five microwave ovens to ship by air. Let’s determine one of them’s parameters:
- length = 53.5 cm, rounded off to 54 cm
- height = 44 cm
- width = 29 cm
Step 2: Determine the Volume of Each Element
Once the measurements are known, multiply the length by the width and the height to find each item’s volume. Next, add up each volume to find the overall volume.
V = 54 cm x 44 cm x 29 cm = 68904 cm3
After converting centimeters to meters, you’ll get 0.0689 m3. Hence, the total volume (five boxes in this instance) is 0.3445 m3.
Step 3: Apply the coefficient
167 is a dimensional weight factor used to convert the cubic meter into kilograms. Hence, the volume is 0.3445 m3 x 167 = 57 kg.
Step 4: Compare the Estimated And Actual Weight
Since one microwave oven with the box weighs 9 kg, the total weight of the five ovens is 45 kg. However, in reality, your shipment will be charged by the carrier as 57 kilograms. Although the difference is negligible in this instance, these numbers can be unexpected when expressed in tonnes of goods.
Important tip: The transport adjustment factor is used to calculate the cubic capacity in the given example, but there is another way to calculate it using a divisor of 5000, as previously stated. In this case, you will get:
54 x 44 x 29 = 68904/5000 = 13.7 (14 kg) * 5 pieces = 70 kg
The method chosen is determined by a number of factors, including the type of transport, the country of shipment or receipt, the manufacturer’s agreements with the logistics company, etc.
Cubic Capacity Rule for LTL and FTL
The cubic capacity rule applies when shipping freight less than a truckload. In general, the LTL carrier stipulates that a shipment is deemed to be overpaying if it occupies more than 750 cubic feet but maintains a density of less than six pounds per cubic foot. On the other hand, a large range of vehicles with varying payload capacities and dimensions ranging from 3.5 tons to 25 tons are available for FTL (Full Truck Load) services.
Benefits of Full Truckload Shipping
Many businesses choose truckload shipping because it offers a number of benefits. Let’s examine each of its main benefits in more detail:
1. Speed
Compared to other shipping methods, TL shipping usually offers faster transit times. Stops to pick up and drop off additional shipments along the route do not cause downtime because the entire truck is devoted to a single load.
2. Cost-effective
TL may be more economical if you ship a lot of goods regularly. With a fixed rate, it is a cost-effective option for larger shipments by enabling businesses to get the maximum value of the space they are paying for. There are various truckload brokerages that help you streamline freight rates.
3. Decreased risk of damage
With truckload shipping, loss and damage during transit are less likely. At the point of origin, the freight is loaded onto the truck, and it is not removed until it arrives at its destination. This helps to ensure a safer transit for your goods by reducing the possibility of mishandling and the resulting damages.
4. Flexibility
TL shipping provides various options to accommodate various shipping requirements. Several truck types are available to accommodate various needs, such as transporting oversized machinery or perishables that require temperature control. These include dry vans, flatbeds, and refrigerated trailers. Due to this flexibility, shippers can customize their logistics plan to meet their specific needs.
5. Direct shipping
TL shipping typically transports goods directly from the pickup location to the destination, excluding the requirement for warehousing or storage. It is a cost-effective option for both short—and long-distance shipments because it reduces storage costs and speeds up delivery times.
6. Increased capacity
TL shipping provides shippers with additional space to accommodate larger shipments because it can fill an entire truck.
Optimize Truck Routes with Nextbillion.ai Truckload Board to Reduce Shipping Rates
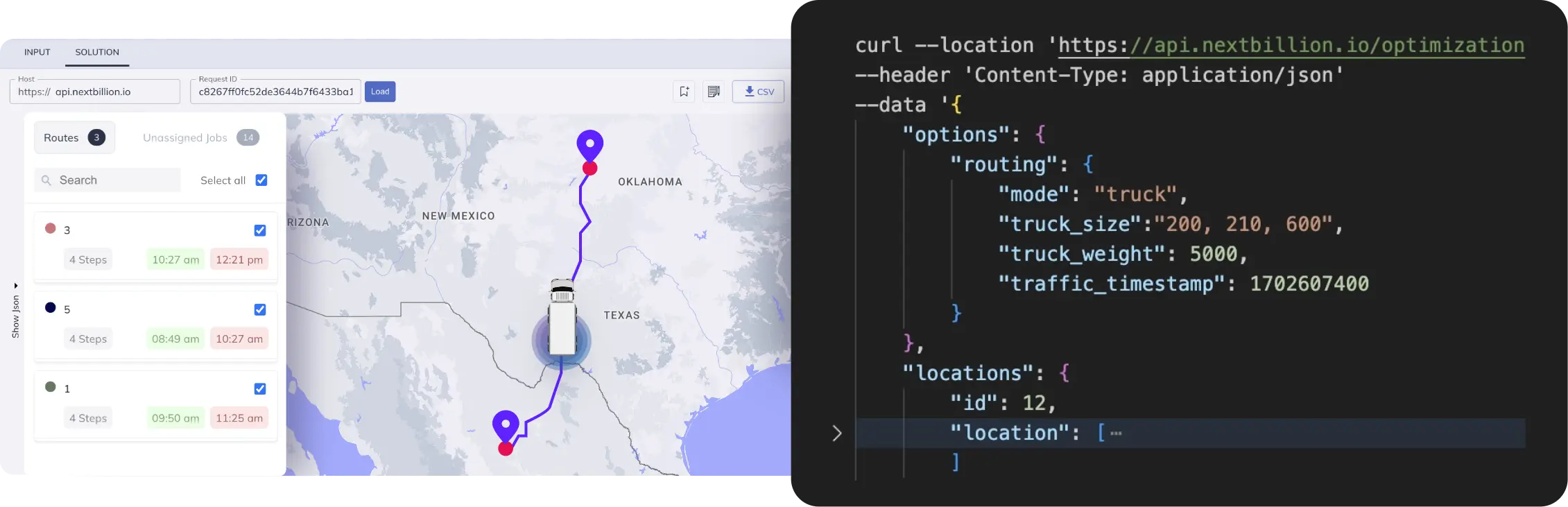
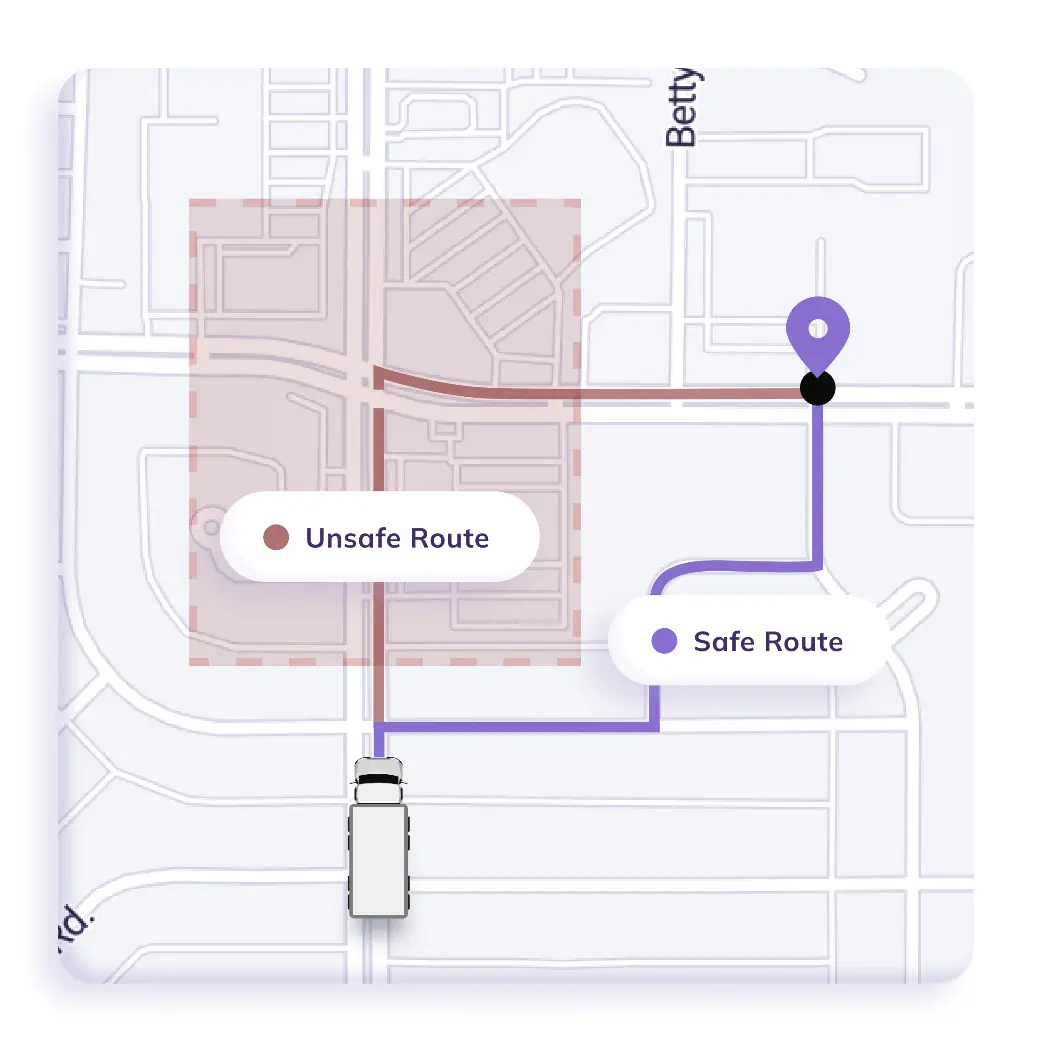
Inefficient routing can become a costly issue for freight services. It affects fuel efficiency, raises schedule accuracy, and increases the risk of missing service level agreement (SLA) responsibilities. Worst of all, customers are frustrated. Transportation route optimization is an effective solution that involves the process of determining the most economical routes for truckloads.
It also serves as a cost-effective option for reducing truckload shipping rates because it decreases fuel consumption. Nextbillion helps logistics companies implement and integrate route optimization in their truckload freight. With our AI-powered Routing and Optimization APIs and SDKs, you can plan multi-location routes that are optimized for truck fleets.
- Get Truck-Compliant Routes: Create routes that adhere to regulations, taking into account the truck’s width and height. Create safe routes for hazmat trucks, making sure they avoid prohibited zones and follow regulations.
- Plan Multi-Day HOS Compliant Routes: Create long-distance routes that adhere to the safety administration’s guidelines for drivers and carriers. Incorporate built-in schedules and breaks to ensure compliance with the Hours of Service regulations for commercial vehicles.
- Optimize Routes With 50+ Constraints: Utilize more than fifty constraints to maximize routes for multiple locations. Schedule routine and recurrent routes, then adjust them to account for unexpected events. Boost productivity in both forward and backward logistics.
- Integrate Your Existing Telematics Vendor: Integrate your current telematics system with ease. Turn on real-time tracking and get immediate notifications for a complete fleet management solution.
- Get Mileage & Speed Limit Violation Reports: Calculate mileage breakdowns by state for taxation, billing, reimbursement, and compliance needs. To assess driver behavior and road safety in your trucking operations, gather information on speed limit infractions.
We ensure that our clients’ logistics operations run smoothly, efficiently, and without any hassles by providing accurate and reliable truckload route optimization. This allows us to provide outstanding service to our clients consistently. Contact us to learn more about Nextbillion.
About Author
Bhavisha Bhatia
Bhavisha Bhatia is a Computer Science graduate with a passion for writing technical blogs that make complex technical concepts engaging and easy to understand. She is intrigued by the technological developments shaping the course of the world and the beautiful nature around us.