

- BLOG
Standardizing Routing Logic Across Global Teams Using APIs
Published: October 9, 2025 | Updated: October 10, 2025
Route Optimization API
Optimize routing, task allocation and dispatch
Distance Matrix API
Calculate accurate ETAs, distances and directions
Directions API
Compute routes between two locations
Driver Assignment API
Assign the best driver for every order
Routing & Dispatch App
Plan optimized routes with 50+ Constraints
Product Demos
See NextBillion.ai APIs & SDKs In action
AI Route Optimization
Learns from Your Fleet’s Past Performance
Platform Overview
Learn about how Nextbillion.ai's platform is designed
Road Editor App
Private Routing Preferences For Custom Routing
On-Premise Deployments
Take Full Control of Your Maps and Routing
Table of Contents

What if every shipment your company planned, from Hamburg to Singapore or New York to Tokyo, followed a consistent, optimized path without delays, redundant detours, or miscommunication between teams? That’s the promise of standardizing routing logic across global logistics operations.
With supply chains becoming international, route planning can mean the difference between a business that is accurate with its deliveries and one that trips along overly expensive inefficiencies. Incorporating enterprise routing policies into APIs will allow businesses to develop a single framework that is efficient, compliant, and reliable all over the regions. This change is transforming the way international teams co-operate in shipping and logistics.
Continue reading to learn about the ways that routing logic, standardized via APIs, reconfigures the workings of the world. Unravel how they function not only in terms of routing, route optimization, and cost reduction but also in terms of customer experience.

In simple terms, routing logic is the set of rules, conditions, and decision-making mechanisms that govern the movement of goods, vehicles, or resources from one place to another. Within a logistics and shipping context, it not only determines the destination of a shipment but also defines the method of transportation, taking into account delivery priorities, vehicle capacities, customs requirements, and regional restrictions.
Routing logic is not optional in global operations. It is fundamental. Without it, multinational logistics teams often fall back on ad hoc planning that results in inefficiencies, inconsistent service levels, and increased costs. By standardizing routing rules through an Enterprise Routing Logic API, organizations can ensure that shipments follow optimal routes, avoid unnecessary delays, and comply with international trade regulations.
That is why routing logic is so critical for global logistics and shipping companies:
Let us understand it via an example:
Suppose a transport company is shipping containers between Hamburg and Singapore. Without consistent routing logic, one regional team might add unnecessary port stops while another ignores customs requirements. The result is a five-day delay and expensive demurrage. By contrast, a Global Team Logistics API ensures every team follows the same routing framework. The API automatically selects the most efficient route, accounts for compliance regulations, and provides unified instructions across regions. The outcome is faster transit times, reduced fuel consumption, and lower handling costs.
This is why standardizing routing logic for logistics companies is not only a technical improvement but a strategic necessity for staying competitive in today’s global supply chains.
Any efficient route of delivery in the world of logistics and shipping starts with a powerful system of regulations and limitations. The basis of route optimization is routing logic, since it provides the circumstances in which optimization systems are executed. Primary parameters like delivery priorities, vehicle capacity, and customs requirements, as well as regional restrictions, are encoded into the routing logic. These parameters make routing logic generate efficient routes and also routes that are in line with international trade regulations.
The contemporary API to solve route optimization in logistics and shipping is based on routing logic to generate dynamic and data-driven decisions out of the static planning stage. After defining routing rules, the optimization engines are used to optimize real-time variables such as traffic movement, weather conditions, fuel prices, and port congestion. This creates paths that are not merely fast and cost efficient, but are also legally sound and resistant to disruptions.
Routing logic has evolved beyond simple pathfinding. Nowadays, it combines warehouse location choice with vehicle route plans to develop a comprehensive logistics system. This is particularly important with cold chain logistics, when the shipments can include mixed cargo with different handling requirements. Variables that are considered in routing logic include delivery time windows, facility proximity, as well as the type of vehicle (standard, refrigerated, or frozen) to reduce the cost of storage and transportation.
As an example, the API that manages routing logic in an enterprise can also consider warehouse locations and vehicle routes, and thus deliver perishable goods within the necessary temperature conditions and with minimal travel distance and fuel consumption. Such integration minimizes investment in facilities in terms of capital and minimizes operational costs in terms of transportation.
Global logistics is not often performed in foreseeable conditions. Traditional optimization presumes that travel times are constant, yet in reality there is uncertainty due to customs inspections, unforeseen weather changes, or traffic jams. To cope with this, routing logic is used to include probabilistic models, including Probabilistic Traveling Salesman Problem (PTSP) and Stochastic Traveling Salesman Problem (STSP).
The models assist companies in creating resilient routes to disruptions through inclusion of probabilities of delays. Through APIs of uncertainty logic application, logistics providers are competent to dynamically reroute shipments in case of disruptions to maintain on-time delivery and reduce penalties.
The technologies of knowledge graphs and generative AI are used to enhance advanced global shipping routing. Knowledge graphs simulate the intricate connections among actors of the supply chain, transport modes, regional restrictions, as well as regulatory demands. Generative AI then completes or fills in missing or incomplete data and introduces alternative multimodal routes that are optimized not only in cost and speed, but also in sustainability.
As an example, AI-based APIs are able to propose alternative routing options that reduce carbon emissions through the combination of ocean and rail transportation instead of automatically switching to air. This provides logistics companies that have dedicated themselves to ESG objectives, while remaining operationally efficient, with a competitive advantage.
The modern operations of global logistics include various priorities that are not centered on cost and distance. The use of modern routing logic with big data facilitates multi-objective optimization. It allows companies to strike a balance between issues like service time windows, level of customer priority, aging of orders, and reduction of emissions.
Through space and time clustering techniques, routing APIs are able to batch shipments, sequence deliveries, and dispatch entire fleets at scale within countries and regions. This guarantees that thousands of shipments can be optimized in one configuration that will provide quantifiable gains in fleet utilization, cost management, and dependability of delivery.
Setting routing logic is a strategic operation which translates business needs into functional guidelines of logistics and shipping networks. It establishes parameters, constraints, and decision-making models that direct optimization engines and APIs. With the ability to directly embed these conditions into an Enterprise Routing Logic API, companies are able to guarantee the full compliance, efficiency, and uniformity of every route among global teams.
Routing logic is fundamentally the codification of business policies and business facts into business rules. Such rules are then run by route optimization engines which deal with the input parameters (static), including vehicle capacity, and input dynamism (live traffic or port congestion). This process ensures that logistics companies are optimized to ensure compliance and scalability across borders in addition to optimizing cost and speed.
The routing logic setting process can normally be described as follows:
The basic variables by which daily logistics operations occur are initially coded in routing logic:
In addition to simple parameters, businesses set their own custom rules that include business-specific policies:
After routing logic has been established, the optimization engine takes the inputs and destination information and calculates and maintains the most efficient routes to use by the fleet or workforce. The routing logic can be updated based on feedback or new operational requirements so that it can be flexible and responsive to business objectives.
Setting routing logic is a strategic operation that ensures that routes are cost effective, within constraints, and sufficiently flexible to accommodate varying delivery environments. Using routing logic in APIs, companies are able to handle complex logistics environments at scale in a more reliable and fast way.
APIs are often used as the intermediary between business rules and optimization engines. They transform operational needs like delivery windows, vehicle capacity, or customs restrictions into request parameters. The API also automatically applies such conditions when optimizing routes, as opposed to manually applying them.
Such standardization does away with human error and makes all routes use the same preprogrammed logic that may be run in Europe, Asia, or North America.
In the background of the API, there are potent optimization solvers that perform the calculations required to come up with efficient routes. These include:
It requires the user to feed in input parameters, and the API executes itself, providing optimized results within seconds.
APIs are connected to live data streams to make routing logic relevant and responsive. APIs automatically reconsider and revise routing decisions by retrieving information like highway conditions, weather data, port congestion, and fuel prices.
This allows real-time dynamic re-routing to help logistics companies prevent delays, lower fuel expenses, and still keep service-level promises even in unforeseen circumstances.
Global logistics entails a compromise of various priorities at the same time. Multi-objective optimization with APIs takes into consideration:
The APIs calculate trade-offs automatically by using tools like evolutionary algorithms or Pareto front analysis and provide the solution in the form of balanced route plans in real time. This ensures that companies do not have to lose one vital aspect, such as service reliability, to gain another, such as cost reduction.
APIs provide common route plans in JSON, XML, or GIS instead of each team developing and interpreting routes uniquely. This provides a standardized framework that can be used by global teams, ensuring that misalignment does not exist because identical operations are carried out across regions.
Standardizing outputs guarantees efficiency in a company and also bestows transparency, because all stakeholders have access to the same optimized routing data.
APIs are easily integrated into business systems like Transportation Management Systems (TMS) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. When a new order is made or an order update is made, workflow triggers call the API to create optimized routes automatically.
This eliminates any manual planning that is required, decision-making is faster, and optimization is built into daily operations.
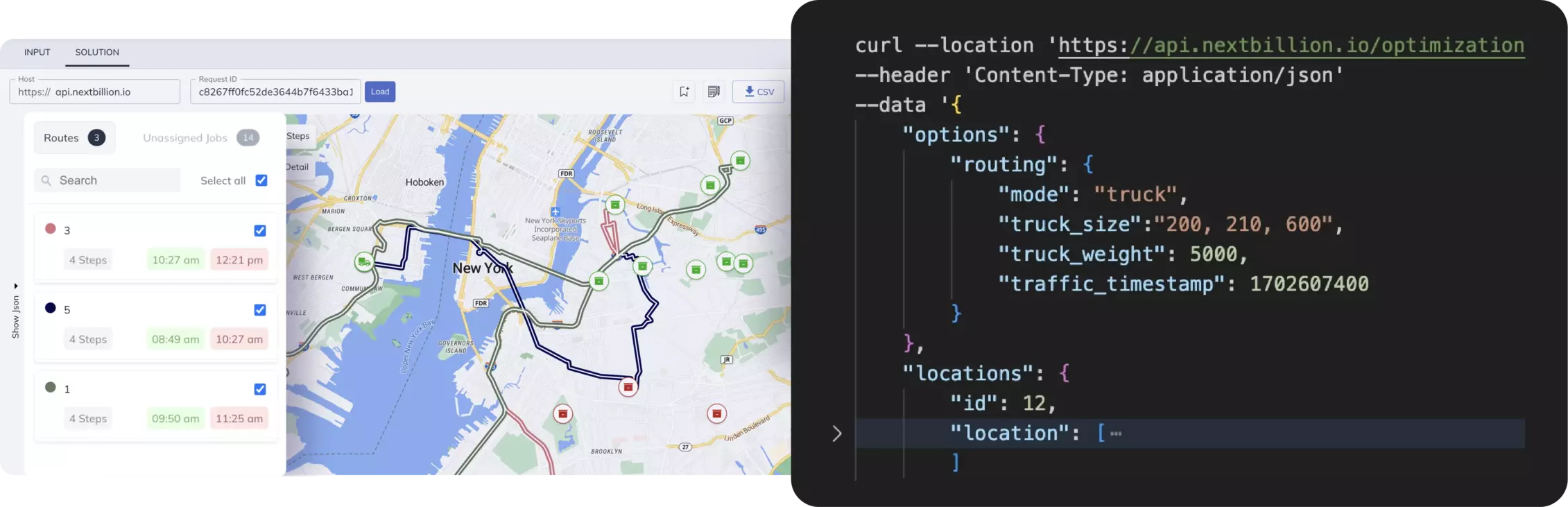
The Global Team Logistics API of NextBillion.ai is a routing optimization API that uses advanced algorithms to resolve routing problems, including single-vehicle routing, multi-vehicle routing, field service, and delivery, which are specifically tailored to logistics and delivery requirements.
The route optimization API tackles the Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP), producing optimal results using multiple vehicles, jobs, locations, depots, and shipments, and addressing numerous operational constraints at the same time. It makes use of programmable optimization engines that integrate heuristics and metaheuristics, for example clustering, route combining, and cost reduction techniques, to optimize efficiency in realistic logistics and shipping networks.
Both hard and soft constraints may be defined by users, and they include:
The routing logic is dynamic to the custom cost matrices. It can be user-defined on travel costs, and varies routes based on altered operational information. The flexibility permits agreement, performance, and dependability throughout global shipping routing activities.
The Enterprise Routing Logic API at NextBillion allows very precise route planning based on multi-dimensional parameters, including:
This ensures that fleet resources and rules of operation are optimized at the same time, making the overall utilization better.
NextBillion has comprehensive tutorials and documentation on how logistics teams can implement shipping API integration for route optimization into their own systems. Examples include:
Explore More: NextBillion Route Optimization API Documentation
Also, go through: Route Optimization Tutorials

The future of logistics is based on the standardisation of routing logic that will introduce efficiency, compliance, and scalability of global operations. With the integration of business rules into an Enterprise Routing Logic API, businesses can guarantee that all the shipments are delivered via the optimal and uniform paths that minimize expenses and enhance the dependability of delivery.
Regardless of whether it is global shipping routing, shipping API integration into enterprise systems, or advanced optimization algorithm application, routing logic is the root of resilience and the supply chains of tomorrow. Using the Global Team Logistics API, companies leave manual operations behind to develop well-streamlined, automated, and standardized logistics operations.
General Routing is ready to revamp your routing operations? See what NextBillion.ai can do with your global teams: use its API to drive efficiency, compliance, and scalability in the optimization of your logistics and shipping routes.
The system of rules, parameters, and decision-making which control routing in logistics networks is called routing logic. The process results in shipments of logistics companies being routed efficiently, meeting the customs and regulatory requirements, and attaining better accuracy in the performance of delivery.
Shipping and logistics route optimization APIs serve as a layer that puts the same routing rules into operation in all regions. Teams in Europe, Asia, and North America utilize the same delivery time windows, vehicle capacity policies, and customs limits by means of an Enterprise Routing Logic API. This eliminates misalignment and brings about global operating uniformity.
Combining API integration to optimize routes with a Transportation Management System (TMS) allows companies to automate processes, including order creation, shipment updates, and route planning. This integration decreases the amount of manual planning, automatically recalculates routes based on live traffic or weather conditions, and enriches fleet utilization and customer service levels.
The routing logic APIs are compatible with most large enterprise systems, including SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, and custom-built ERP or TMS. These integrations directly incorporate optimization as part of day-to-day business, which makes global logistics teams consistent, compliant, and efficient using a single Global Team Logistics API.
Bhavisha Bhatia is a Computer Science graduate with a passion for writing technical blogs that make complex technical concepts engaging and easy to understand. She is intrigued by the technological developments shaping the course of the world and the beautiful nature around us.