Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Skill-based routing is a game-changing strategy that matches the right task with the most qualified personnel, ensuring that jobs are completed swiftly and accurately. This ultimate guide dives into the mechanics of skill-based routing, exploring how it enhances route planning, optimizes resources, and leads to seamless operations. Whether you’re a logistics manager or a business owner, mastering this approach will give you a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
What is Skill-Based Routing?
Skill-Based Routing (SBR) is a method used to match tasks with the most qualified individuals based on specific skills. This approach ensures that tasks are handled by those best equipped to manage them, leading to more efficient operations.
In modern logistics and customer service, SBR is crucial. It streamlines processes, reduces errors, and enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring that the right person handles the right task at the right time.
It improves business efficiency, optimizes resource use, and elevates service quality. For your business, SBR can mean faster task completion, better customer experiences, and improved team performance.
This guide will provide an overview of SBR, its benefits, and practical insights on how to implement it effectively. Whether you’re looking to optimize your operations or improve customer satisfaction, understanding SBR is essential.
What is the Need for Skill-Based Routing?
Skill-Based Routing (SBR) is essential for optimizing operations while delivering a superior customer experience. By ensuring that tasks are matched with the right skills, businesses can achieve higher efficiency, accuracy, and overall effectiveness in their operations.
Efficiency & Accuracy:
SBR ensures that tasks are assigned to individuals with the necessary skills, leading to more efficient and accurate execution. For instance, in field service operations, technicians with specific expertise handle equipment or service requests they’re best suited for, minimizing errors and increasing productivity.
Customer Satisfaction:
Assigning skilled personnel to tasks not only improves the quality of service but also ensures timely job completion. Skilled workers are more efficient, resulting in quicker service and better adherence to Service Level Agreements (SLAs). This directly impacts customer satisfaction by reducing errors and ensuring a smooth, high-quality service experience.
Resource Optimization:
Properly matching skills to tasks reduces operational costs. By enhancing first-time fix rates and minimizing repeat visits, SBR contributes to cost efficiency and better resource utilization, which is crucial for maintaining a lean, effective operation.
Compliance and Safety:
In industries requiring specific certifications or qualifications, SBR ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. Additionally, by assigning the right skilled workers, businesses can reduce the risk of accidents and ensure that safety protocols are followed, which is vital for both legal compliance and employee well-being.
Employee Satisfaction:
Employees are more motivated and satisfied when they are assigned tasks that align with their skills and qualifications. This leads to higher job satisfaction, better performance, and increased retention rates, which are critical for maintaining a skilled and engaged workforce.
Business Reputation:
Consistently delivering high-quality service through SBR enhances a company’s reputation. A strong reputation attracts new customers, fosters loyalty, and opens up new business opportunities, positioning the company as a leader in its field.
Skill-Based Routing is a powerful approach that drives efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances both customer and employee satisfaction. By leveraging SBR, businesses can achieve a competitive edge, build a stronger reputation, and ensure long-term success.
Basics of Skill-Based Routing
Skill-Based Routing (SBR) is a feature in route planning that ensures tasks are matched with the right vehicles or drivers based on specific skills. This process is vital for executing tasks efficiently and accurately, particularly in complex logistics and dispatch operations.
Fundamental Concepts
In routing, “skills” refer to the qualifications or capabilities that a driver or vehicle must have to complete a task. These could include technical expertise, certifications, or specific vehicle capabilities. For example, a task requiring the transport of hazardous materials would need a driver with hazardous material certification and a vehicle equipped to safely handle such cargo.
How Skill-Based Routing Works
SBR operates on the principle of strict matching. Each task is assigned a set of required skills. Similarly, each vehicle or driver in the fleet is tagged with the skills they possess. The routing optimizer then matches tasks to vehicles or drivers based on these skills.
Multiple Skills Matching: A task can require multiple skills. For the task to be assigned, a vehicle or driver must possess all the skills specified. If a driver or vehicle lacks even one of the required skills, they will not be assigned the task.
Hard Filter: Skill matching is a hard filter in SBR. If no available vehicle or driver matches all the required skills for a task, that task will remain unassigned in the final routing plan. This ensures that tasks are only assigned when they can be executed with the required expertise, reducing the risk of errors or incomplete service.
Examples of Skill-Task Matching
Consider a delivery operation where some tasks require refrigeration and others need handling of fragile items. Vehicles with refrigeration capabilities are assigned to cold-chain tasks, while vehicles equipped for careful handling are assigned to fragile item deliveries. If a task requires both refrigeration and fragile handling, only a vehicle possessing both skills will be assigned that task.
By ensuring that only the right vehicles or drivers are assigned to tasks, Skill-Based Routing enhances the accuracy and efficiency of dispatch operations. This results in more reliable service delivery, better resource utilization, and improved customer satisfaction.
Is Skill-Based Routing Legally Required?
In certain industries, Skill-Based Routing (SBR) is not just a best practice—it’s a legal requirement. These mandates are designed to ensure safety, regulatory compliance, and the use of qualified personnel for specific tasks.
Healthcare
In healthcare, skill-based routing is essential for compliance with legal standards. Home care assignments, for example, must be handled by licensed medical professionals such as nurses or anesthesiologists. Performing medical procedures without the proper licensing can lead to severe penalties, including loss of license and legal action.
Construction and Utilities
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates that only qualified and trained personnel perform specific tasks, such as operating heavy machinery or working with electrical systems. Non-compliance can result in fines and increased liability for workplace accidents. Additionally, certain tasks require specific certifications, like welding or handling hazardous materials, to ensure safety and legal compliance.
Transportation and Logistics
Drivers transporting hazardous goods must have a Commercial Driver’s License (CDL) with a HazMat endorsement. Failing to assign such tasks to properly licensed drivers can lead to legal consequences and jeopardize the safety of the operation.
Field Services
Field service technicians often need technical certifications to perform tasks like repairing HVAC systems, installing electrical systems, or servicing medical equipment. Assigning tasks to unqualified personnel not only risks service failures but also exposes the business to significant legal liabilities.
In these industries, adhering to skill-based routing isn’t optional—it’s a legal necessity to ensure compliance and protect both the business and its employees from legal and financial risks.
Key Components of Skill-Based Routing
Skill-Based Routing (SBR) is built on two fundamental components: identifying relevant skills and effectively matching those skills to tasks. These elements are crucial for optimizing routing and dispatch operations.
Identifying Skills
The first step in implementing SBR is to identify the skills relevant to your operations. These skills vary across industries but are generally tied to the specific tasks that need to be performed.
Common Skills in Routing and Dispatch:
Technical Expertise: Required for tasks like machinery repair or IT support.
Certifications: Necessary for handling hazardous materials or operating specialized equipment.
Language Proficiency: Important for customer service roles in multilingual environments.
Vehicle Capabilities: Such as refrigeration for cold-chain logistics or lift capacity for heavy loads.
Matching Skills to Tasks
Once the relevant skills are identified, the next step is to align these skills with the tasks that need to be completed. This process ensures that each task is assigned to the most qualified individual or vehicle, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
Alignment Process:
Task Requirements: Define the specific skills needed for each task.
Skill Mapping: Use a skill matrix to match available skills with the requirements of each task.
Simple Algorithms and Tools:
Rule-Based Algorithms: These are used to create simple if-then rules that automatically match tasks to available resources based on skill requirements.
Optimization Software: Advanced tools can automatically assign tasks by considering multiple factors, including skill matching, availability, and route efficiency.
How to Include Skill-Based Routing in Your Business Operations?
Integrating Skill-Based Routing (SBR) into your business operations is essential for enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Nextbillion.ai offers a robust Route Optimization feature that allows you to seamlessly incorporate SBR into your workflow.
Specify Task Skills
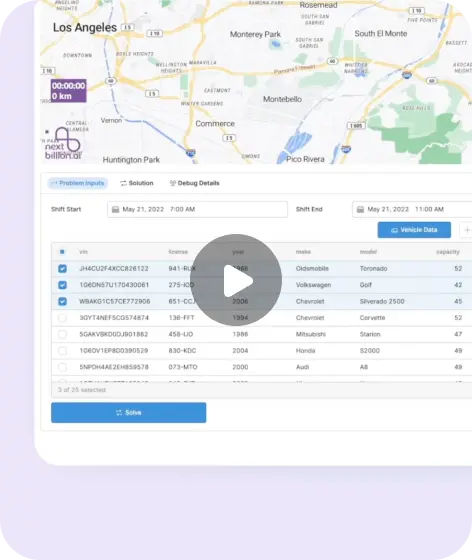
Begin by defining the specific skills required to complete each task within your operations. Our Route Optimization API allows you to specify one or multiple skills per task, ensuring that all necessary qualifications are covered.
Define Vehicle/Driver/Agent Skills
Next, input the skills that your vehicles, drivers, or agents possess. This step is crucial for ensuring that the system has accurate data to match tasks with the appropriate resources.
Optimization Process
During the optimization phase, our tool will automatically match the skills required for each task with the skills available in your fleet. Only vehicles, drivers, or agents that possess all the required skills for a particular task will be assigned to it. This ensures that tasks are completed correctly and efficiently.
Unassigned Tasks: If a task requires skills that no vehicle, driver, or agent in your fleet possesses, it will remain unassigned. This feature ensures that tasks are not allocated to underqualified personnel, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Integration with Route Planner
This Skill-Based Routing feature is fully integrated with our Route Planner web application, making it easy to incorporate into your existing operations. Whether you’re managing a small fleet or a large operation, our tool ensures that every task is handled by the most qualified resource available.
By utilizing Nextbillion.ai’s Skill-Based Routing, you can optimize your routing and dispatch processes, enhance service quality, and ensure that every task is matched with the right expertise. This not only improves operational efficiency but also boosts customer satisfaction and compliance with industry regulations.
About Author
Rishabh Singh
Rishabh Singh is a Freelance Technical Writer at NextBillion.ai. He specializes in Programming, Data analytics and technical consulting, turning complex tech into clear and engaging content.