Table of Contents
Reverse logistics, also known as reverse distribution, is a phase in the supply chain where products move back from the point of sale to the manufacturer or distributor for purposes such as recovery, repair, recycling, or disposal. It involves all processes associated with the backward flow of products and materials within the supply chain. It refers to the movement of goods from their usual final destination to recapture value or ensure proper disposal. Unlike forward logistics, where products travel in a predictable path from manufacturers to consumers, reverse logistics involves complex, often unpredictable routes, leading to higher operational costs and inefficiencies.
Reverse Logistics Process
Keys steps that are involved in the Reverse Logistics Process in general are:
- Initiating the Return: Return requests are initiated due to different reasons such as defects, incorrect shipments, warranty claims, or end-of-life product recycling. These returns can be grouped under Customer Returns, End-of-life Returns, and Warranty Returns.
- Determining the return category and verifying the reason for return: The reason for the return and the return group under which the return is initiated are verified to determine the eligibility.
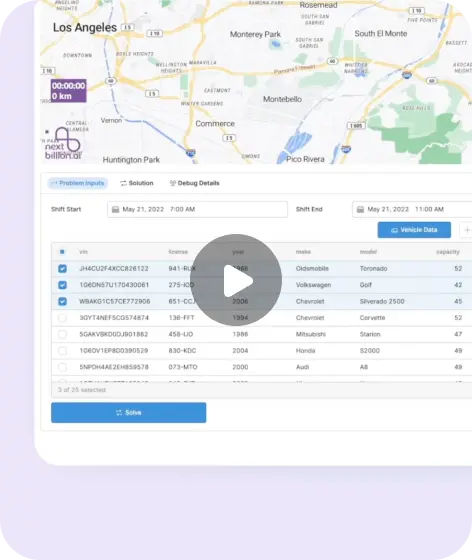
- Product (return) collection and its transportation: The product is collected from the customer or the distribution center. Logistics handle the transportation to the return centers. Efficient Route Optimization ensures the timely return processing.
- Inspecting the return product: The returned product is quality checked for any defects and resale potential. Sorting decisions are made in this phase where they are categorised based on the product’s quality. Accordingly, they are sorted in the Restocking (if the product is in good condition), Refurbishing (if minor repairs are needed), Recycling (if it is beyond repair) or Disposal (if unusable) categories.
- Processing the return product: Processing of the categories mentioned in the above point begins here.
- Initiating the refund: Refund process begins here and the customers receive their refunds depending on the return policy.
- Analysis: In this phase companies analyze the return patterns to identify the cause and implement strategies to reduce return costs and hence improve efficiency.
Types of Reverse Logistics

- Returns management: Returns management, also known as customer returns, involves processing product returns due to defects, incorrect shipments, or customer dissatisfaction. For example, an e-commerce customer may return a pair of shoes that don’t fit.
- Remanufacturing and Refurbishing: Remanufacturing and refurbishing involve repairing, restoring, or upgrading returned or used products to make them suitable for resale. For instance, a laptop returned under warranty may undergo refurbishment and be resold as a certified pre-owned device.
- Recycling and Waste Management: Recycling and waste management involve recovering materials from used products to reduce environmental impact. For example, old smartphones are collected, and their components, such as lithium batteries and metals, are extracted for recycling.
- Repackaging and Resale: Repackaging and resale involve preparing returned but unused products for resale by ensuring they meet quality standards. For instance, an unopened smartphone that has been returned is inspected and then resold at a discounted price.

The Growing Importance of Reverse Logistics
Implementing an efficient reverse logistics process is crucial for maintaining a seamless and successful supply chain. Modern consumers prioritize convenient return policies, leading to a significant increase in e-commerce return rates three to four times higher than in-store purchases. As a result, effective reverse logistics solutions are essential for enhancing customer satisfaction, fostering loyalty, and mitigating financial losses associated with returns.
With returns amounting to nearly a trillion dollars annually worldwide, businesses that master reverse logistics can recover lost revenue, strengthen customer relationships, and encourage repeat purchases. By streamlining reverse logistics operations, companies can transform returns from potential setbacks into opportunities, ultimately improving the customer experience and unlocking substantial financial advantages.
Some factors that are driving the need for better reverse logistics could be consumer expectations, cost implications, sustainability goals, regulatory compliance and so on.
Benefits of Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics plays a crucial role in various industries, helping businesses efficiently manage returns, reduce waste, and improve sustainability. Below are the key benefits based on industry-specific applications:
- E-Commerce: In the e-commerce industry, where return rates are significantly high, an efficient reverse logistics process is essential for minimizing costs and enhancing operational efficiency. By streamlining the return process, businesses can reduce expenses associated with product returns while ensuring a seamless experience for customers. Hassle-free return policies and quick refunds contribute to greater customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. Additionally, effective inventory management strategies—such as reselling, refurbishing, or repurposing returned items—help optimize stock levels and reduce financial losses, making reverse logistics a crucial component of a successful e-commerce business.
- Automotive Industry: In the automotive industry, effective reverse logistics plays a vital role in reducing manufacturing costs by refurbishing and reusing components, thereby minimizing the need for new production. Recycling materials such as metals, plastics, and rubber not only supports sustainability efforts but also helps conserve resources and reduce waste. Additionally, proper handling and disposal of hazardous materials ensure compliance with environmental regulations, protecting both the business and the environment. By implementing efficient reverse logistics strategies, automotive companies can enhance cost efficiency, sustainability, and regulatory adherence.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: In the pharmaceutical industry, an effective reverse logistics process is essential for ensuring regulatory compliance by efficiently managing product recalls to prevent health risks. Proper handling of expired or defective medications safeguards brand reputation and maintains consumer trust. Additionally, recycling and reusing pharmaceutical packaging materials help reduce waste, contributing to sustainability efforts. By implementing robust reverse logistics strategies, pharmaceutical companies can enhance safety, minimize environmental impact, and uphold industry standards.
- Consumer Electronics: In the consumer electronics industry, reverse logistics plays a crucial role in extending the product lifecycle by repairing and reselling refurbished devices. By recycling components such as batteries and circuit boards, companies can significantly reduce electronic waste (e-waste) and contribute to environmental sustainability. Additionally, the resale of certified pre-owned devices creates new revenue streams, making refurbishment and recycling both a profitable and eco-friendly strategy for businesses in the sector.
- Retail Sellers: For retail sellers, managing high volumes of returns efficiently is essential for maintaining smooth operations and customer satisfaction. By implementing effective sorting and restocking processes, businesses can improve inventory control and optimize product availability. Well-structured return policies and streamlined logistics solutions help reduce operational costs while ensuring a hassle-free return experience. Providing seamless returns not only enhances customer retention but also strengthens brand loyalty, making reverse logistics a key component of a successful retail strategy.
- Reusable Packaging Industry: In the reusable packaging industry, reverse logistics helps lower production costs by reusing materials like plastic containers and pallets, reducing the need for constant new production. This approach supports sustainability by minimizing waste and promoting eco-friendly practices. Additionally, by establishing a circular economy for packaging materials, businesses can enhance supply chain efficiency, ensuring a cost-effective and environmentally responsible packaging solution.
Challenges in Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics presents several challenges that businesses must navigate to optimize efficiency and reduce costs.
Collecting, Sorting, and Processing Returns
This involves high labor and operational costs for handling returns, need for self-service return solutions to reduce expenses, and complex sorting, inspection, and repackaging processes.
Managing Long-Distance Returns
Increased transportation costs and risk of damage, impact on profitability and environmental footprint, and need for optimized routes and local drop-off points.
Inventory Management Complexities
Difficulty in forecasting return volumes, challenges in assessing item value, condition, and refurbishment status, and need for real-time tracking and analytics for efficient processing.
Lack of Standardized Returns Policies
Complicated processing due to inconsistent policies, high return fraud costs over $84.9 billion annually, and need for clear policies to improve efficiency and customer trust.
Integration With Existing Supply Chain Software
Reverse logistics should align with forward supply chain operations, complexities in tracking the impact of returns on profitability, and essential for businesses transitioning to a circular economy model.
High Transportation, Processing, and Storage Costs
Transportation accounts for up to 60% of reverse logistics costs, expensive refurbishment, repackaging, and disposal processes, and necessity for efficient logistics planning to minimize expenses.
Resource Allocation & Operational Efficiency
Additional workforce needed for receiving, sorting, and refurbishing returns, rising labor costs for customer service and warehouse operations, and automation and AI-driven solutions required to enhance efficiency.
Navigating International and Local Regulations
Compliance with tax, tariff, and return regulations across borders, and handling hazardous materials safely per regional laws, adapting to evolving consumer protection and recall policies.
Compliance With Environmental Standards
Pressure from investors and regulators for sustainability reporting, high costs of recycling vs. landfill disposal, and need for tracking environmental impact alongside cost analysis.
The Role of Route Optimization in Reverse Logistics
To combat the challenges discussed in the previous section, you should leverage advanced algorithms through Route optimization. Route optimization streamlines return pickups and reduces transportation costs. Key benefits include:
Dynamic Route Planning
Dynamic route planning enables the integration of last minute customer requests with existing scheduled orders, allowing real-time adjustments to delivery routes. By leveraging algorithms and advanced technology, it adapts to changing factors such as traffic, weather, and order priorities to optimize efficiency and responsiveness.
Reduced Fuel and Labor Costs
With reduced fuel and labor costs, a company or individual can effectively reduce both fuel related expenses (such as gasoline or diesel for vehicles) and employee wage costs. This is typically accomplished through operational efficiency measures, including optimized routing, fuel efficient vehicles, improved workflows, and employee training.
Efficient Load Balancing
Efficient load balancing process distributes a set of tasks over a set of multiple resources (computing units), with the aim of improving performance and user experience.
Improved Customer Experience
Timely pickups enhance customer satisfaction and streamlines refund/replacement processes. More efficient returns lead to faster product resale or refurbishment, reducing inventory holding costs.
Sustainability and Carbon Footprint Reduction
Reduced fuel consumption aligns with sustainability goals and regulatory compliance. Optimized logistics reduce unnecessary trips, lowering the overall carbon footprint. A carbon footprint is the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions an individual, organization, or product causes. Carbon footprints are calculated for the entire life cycle of a product or service.
Advanced Technologies Driving Reverse Logistics Optimization
Cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, data analytics, and blockchain play a crucial role in enhancing reverse logistics. These innovations automate processes, enable real-time visibility, enhance decision-making, and streamline product recovery, refurbishment, and recycling throughout the returns lifecycle.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI-driven route planning continuously optimizes pickup routes in real time, while machine learning algorithms analyze return patterns to predict volumes and recommend proactive route adjustments for greater efficiency.
Geospatial Intelligence & Mapping
High-precision geocoding enables accurate tracking of pickup locations, while real-time tracking and geofencing enhance logistics transparency and operational visibility.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Connected Vehicles
IoT devices in vehicles continuously track fleet performance and enable dynamic route optimization, while sensors deliver real-time insights into vehicle health, helping to minimize maintenance costs.
Blockchain for Returns Management
Blockchain improves transparency in reverse logistics, minimizing fraud and disputes, while smart contracts automate returns verification and streamline the refund process.
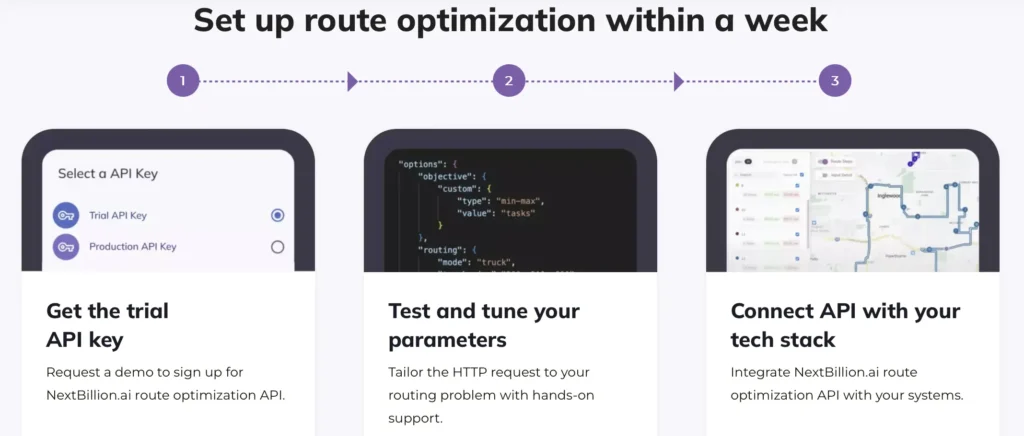
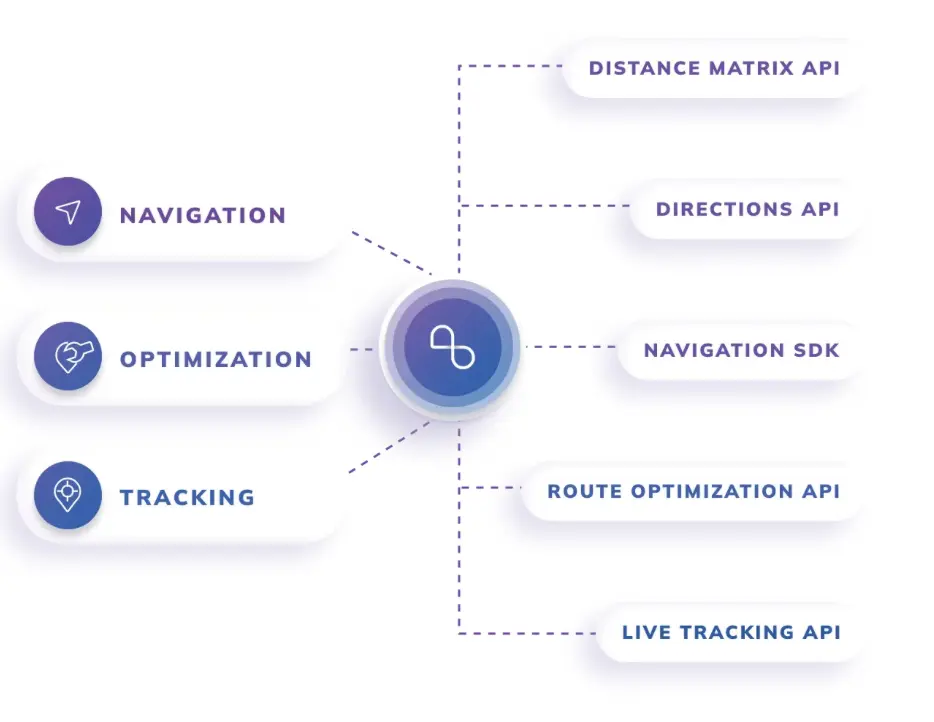
How NextBillion.ai Enhances Reverse Logistics with Route Optimization
NextBillion.ai is transforming reverse logistics with cutting-edge AI-driven mapping and route optimization solutions. NextBillion.ai’s platform is designed to address the challenges of managing returns by offering intelligent, scalable, and highly customizable routing solutions. With a focus on efficiency, cost reduction, and sustainability, NextBillion.ai helps businesses streamline their reverse logistics operations through the following capabilities:
AI-Powered Route Optimization
NextBillion.ai’s customized routing algorithms optimize return pickups based on live traffic patterns, fuel efficiency, and pickup windows. Its advanced predictive analytics anticipate peak return periods, optimizing fleet deployment accordingly.
Read Route Optimization Flexible API tutorials to know basic constraints offered in NextBillion.ai’s Route Optimization Flexible API.
Dynamic and Real-Time Adjustments
NextBillion.ai’s API-driven system recalculates routes in real-time, adapting to cancellations, new return requests, and road conditions. Its dynamic rerouting ensures minimal delays, reducing operational inefficiencies.
Refer here for further information on NextBillion.ai’s Live Tracking API.
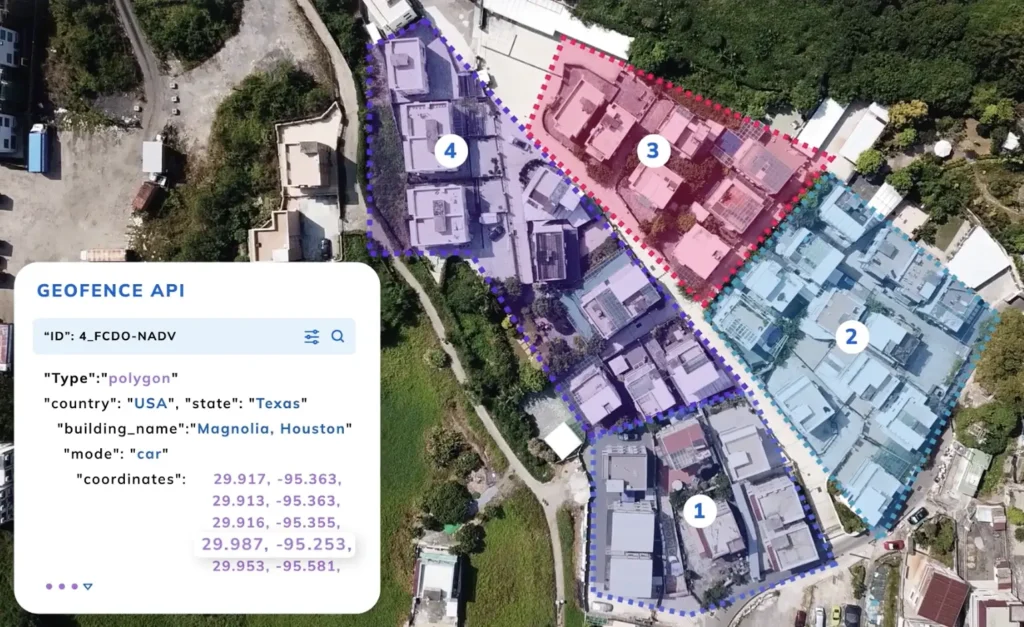
Geospatial Intelligence and Mapping
NextBillion.ai offers highly accurate geocoding and location intelligence, enabling precise pickup location tracking. Its mapping solutions integrate seamlessly with reverse logistics workflows, reducing errors, and enhancing accuracy.
Refer Geofencing API for more information on how logistics services can use the Geofence API to improve their operations, enhance customer experiences, and increase efficiency.
Multi-Stop and Clustered Routing
NextBillion.ai efficiently plans multi-stop reverse logistics routes, grouping returns for optimal fleet utilization. Its cluster-based routing reduces unnecessary trips and improves fleet efficiency.
Seamless API Integration
NextBillion.ai’s scalable APIs integrate easily with existing TMS, WMS, and ERP systems to enhance logistics workflows. It automates dispatching and routing using real-time data from multiple sources.
Sustainability and Cost Savings
NextBillion.ai reduces transportation costs while meeting sustainability objectives through optimized route planning. Its eco-friendly route planning minimizes emissions and fuel consumption.
By leveraging NextBillion.ai’s innovative route optimization technologies, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, cut down logistics expenses, and meet their sustainability goals while improving customer satisfaction in reverse logistics.
Conclusion
For companies looking to reduce return costs, increase sustainability, and boost customer happiness, effective reverse logistics is essential. Route optimization plays a vital role in this process by streamlining transportation, reducing fuel consumption, and improving turnaround times for returned goods. Businesses may greatly improve their reverse logistics operations by integrating cutting-edge technology like blockchain-driven transparency, IoT-enabled real-time tracking, and AI-powered dynamic routing. More accurate geocoding, proactive route modifications based on predictive analytics, and automation of crucial procedures like refund administration and returns verification are made possible by these advancements.
Businesses may reduce operational costs, eliminate inefficiencies, and make sure that returned goods are processed, repaired, or recycled more efficiently by utilizing data-driven decision-making. Beyond just saving money, improved reverse logistics also helps achieve sustainability objectives by cutting waste and carbon emissions. Businesses who invest in intelligent route optimization technologies will have a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced supply chain and e-commerce environments by improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
NextBillion.ai offers a robust suite of AI-powered mapping and route optimization solutions designed for complex logistics operations, including reverse logistics. With highly customizable APIs and SDKs, NextBillion.ai enables businesses to build dynamic routing systems that adapt to real-world conditions such as traffic, weather, and fluctuating return volumes. The platform’s precise geocoding capabilities ensure accurate pickup location tracking, while its real-time data analytics provide actionable insights to streamline return processes.
Additionally, NextBillion.ai supports enterprises in reducing costs through efficient route planning, automated dispatching, and integration with existing logistics infrastructure. Its AI-driven approach helps businesses optimize vehicle utilization, minimize fuel expenses, and enhance transparency in reverse logistics workflows. Whether you’re managing large scale e-commerce returns or optimizing B2B reverse logistics operations, NextBillion.ai empowers businesses with scalable, intelligent solutions to transform their reverse logistics strategy and maximize efficiency.
About Author
Prabhavathi Madhusudan
Prabhavathi is a technical writer based in India. She has diverse experience in documentation, spanning more than 10 years with the ability to transform complex concepts into clear, concise, and user-friendly documentation.