Table of Contents
The oil and gas industry depends greatly on the mapping technology. Without advanced geospatial tools, finding untapped reserves or managing sprawling infrastructure would feel like trying to clear a maze blindfolded. With geospatial mapping technology, companies can precisely pinpoint resources, plan pipelines, and ensure environmental compliance. This blog discusses the role of mapping technology in oil and gas exploration, its applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Key Applications of Mapping Technology

Mapping technology has become central in the oil and gas industry for challenges like locating reserves, maintaining infrastructure, and adhering to environmental regulations. The key applications of mapping technology are listed below:
1. Exploration and Discovery of New Reserves
One of the petroleum industry’s most vital and costly parts is finding new oil and gas deposits. Mapping technology greatly enhances this process by giving the viewer a detailed visualization of complex geological formations. Advanced seismic imaging and satellite data analytics also allow companies to identify potential drilling sites with greater accuracy.
Exploration mapping in the oil and gas industry utilises data from seismic surveys, remote sensing, and GIS about oil and gas at a potential site. This reduces the risks of drilling dry wells, which is costly and environmentally destructive. Seismic data processing software such as Petrel or Kingdom can generate 3D models of subsurface geology. They help geologists identify fault lines, rock layers, and trapped hydrocarbons almost effortlessly.
3D mapping for oil and gas enables detailed subsurface structures to be developed so that geologists can find fault lines, rock layers, and where hydrocarbons might get trapped.
Such imagery further provides satellite views that support the definition of a prospective surface anomaly. Machine learning algorithms applied to satellite data can also help identify surface deformations that indicate underlying resource deposits. The joint application of these technologies enables an exploration team to systematically reduce an immense geological prospect to drillable well positions faster and smarter.
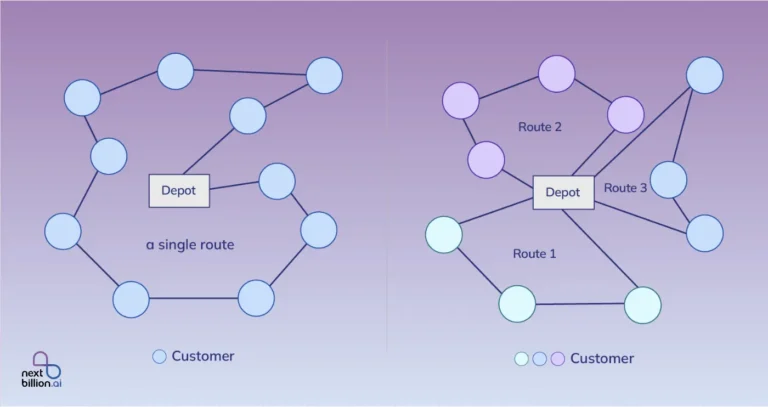
2. Optimizing Pipeline Routes and Infrastructure Planning
The lifeblood of any oil and gas industry consists of pipeline networks that help transfer resources from extraction sites to various processing plants and distribution centres. However, to design and build such networks, one has to balance efficiency, safety, and environmental concerns.
That is where pipeline mapping technology plays its role. Pipeline mapping software, such as GIS-based ArcGIS, helps planners visualize the entire route and calculate the most efficient paths while considering environmental factors.
GIS for oil and gas is important when planning pipeline routes. It considers critical factors that include, but are not limited to, terrain, land ownership, environmental restrictions, and existing infrastructure. For instance, GIS tools enable engineers to plan routes with minimal risk by identifying restricted roads, and landslide or flood-prone areas. They also map areas of ecological sensitivity, thus allowing compliance with local regulations and reducing disturbance to habitats.
3. Monitoring Environmental Impacts and Compliance
Governments and the public are increasingly scrutinizing the oil and gas industry for being more transparent and responsible about its environmental impacts. Mapping technology provides the means to monitor and manage such effects effectively. Remote sensing technologies, including drones with infrared sensors and satellite imagery, allow for continuous monitoring of ecological zones impacted by oil and gas operations.
Real-time mapping, especially with drones and UAVs, allows companies to run frequent and accurate environmental surveys. Systems with infrared cameras fitted on drones detect oil spills or gas leaks at pipelines, even at remote or hazardous locations, and provide real-time feedback so that companies can swiftly take measures to contain the damage in the shortest time.
Data visualization in oil and gas is also great for communicating environmental performance to stakeholders. Companies can present data through intuitive maps and dashboards that clearly outline efforts to:
- Reduce emissions
- Protect biodiversity
- Abide by regulations
- Contribute to the community
Types of Mapping Technologies Used
From GIS to real-time drone mapping, the industry has embraced many technologies that help develop new ways to improve exploration, planning, and monitoring. Every tool has its unique features and benefits. Some of the tools include:
1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)

Mapping technology in oil and gas is the backbone of GIS. It integrates spatial and non-spatial data into one comprehensive map that helps in exploration, planning, and risk management. GIS platforms like ESRI ArcGIS and QGIS allow companies to overlay geospatial data with existing operational systems to enrich decision-making. Be it terrain analysis or infrastructure mapping, GIS has a solution to suit the industry’s customised needs.
2. Remote Sensing and Satellite Imagery

Satellites can click up top images of our earth, and these pictures are highly useful for exploration and environmental monitoring. Moreover, oil and gas mapping software using remote sensing can identify minute changes in vegetation, soil composition, and surface structures that can often point to underlying resources.
3. 3D and 4D Subsurface Mapping Technologies
From traditional 2D maps, the industry has moved to immersive 3D mapping for oil and gas, which models subsurface structures in incredible detail. Adding the time dimension in 4D mapping lets a company understand changes in the reservoir conditions over time, optimising the decisions in the production phase.
Top Benefits of Mapping Technology
Advanced mapping solutions are implemented to get noticeable benefits. Here are some of the major benefits:
1. Improved Resource Estimation Accuracy
Accurate resource estimation is the bedrock of oil and gas operations. Advanced geospatial mapping solutions, like 3D mapping, let companies identify and quantify reserves with a high accuracy rate. AI algorithms integrated into GIS systems analyze seismic data and geological surveys to pinpoint the most promising drilling locations. They eventually improve the success rate of exploration.
Unlike conventional methods, these technologies can provide highly specific details about subsurface structures, minimising the chances of drilling dry wells. Such functionalities combine geology-based data and their spatial details to enable operators to visualise how the resources are distributed easily.
2. Improved Safety and Risk Management
The oil and gas industry is filled with risks, from equipment breakdowns to environmental tragedies. Real-time mapping solutions are necessary for spotting risks before they escalate.
Real-time hazard mapping tools can instantly alert on-site personnel during any emergency, supporting quick action to protect employees and facilities. By proactively handling risks, companies can avoid accidents and build a culture of safety, which is necessary to retain public trust and employee morale.
3. Cost Efficiency in Operations and Logistics
Efficiency and cost-saving go hand in hand in the oil and gas industry. Mapping software for oil and gas is game-changing for cost efficiency, just like route optimization is for logistic operations. From planning pipeline routes to fleet operations, mapping technologies can streamline complex processes and significantly reduce operational expenses.
Take pipeline construction, for instance. With pipeline mapping technology, cost routes can be found, which means that they can avoid hard-to-reach terrain or highly populated areas altogether. Similarly, route optimization APIs streamline fleet management by developing efficient transportation routes and minimizing vehicle fuel consumption and wear and tear.
4. Empower Data-Driven Decision-Making
In the oil and gas industry, fast decision-making with informed choices remains the biggest bullet in the competition arsenal. Mapping technologies, such as geographic information systems in oil and gas mapping, provide a range of data that can be analysed and visualised as outputs that support strategic decisions.
For example, bringing together live traffic data, environmental conditions, and logistics restrictions in one map allows decision-makers to optimise supply chain operations. Such detailed insight ensures decisions are always based on the most accurate and timely information, hence minimising the possibility of making costly mistakes. More importantly, data visualization in oil and gas helps translate big data into actionable insights across teams and various departments in harmony.
Implementation Challenges of Mapping Technology
While mapping technology in oil and gas presents great benefits, there is certainly no plain sailing. Challenges mainly lie in how these state-of-the-art technologies could be effortlessly integrated into the industry that conventionally relied upon legacy systems. Some of these challenges are mentioned below:
1. High Initial Costs and Training Requirements
Among the key entry barriers for companies wanting to use advanced mapping software in oil and gas will be financial barriers. Buying advanced tools like 3D mapping of oil and gas, remote-sensing equipment, and drone-based mapping systems means very high upfront capital investment. Apart from the tool cost, an organization must implement and maintain the system with frequent periodic upgrades.
Moreover, most of these systems require employees to undergo specialised training to use them. This is even more the case with complex technologies such as GIS in oil and gas, which requires deep knowledge of geospatial analysis and the operational context of the oil and gas industry. Training programs can be quite time-consuming and expensive, thus possibly slowing down the adoption rate and lowering productivity during the learning curve.
2. Integration with Legacy Systems
Legacy systems, most developed long ago, have dominated traditional operations in the oil and gas industry. Many of these older systems were not designed to interface with modern mapping technologies, creating compatibility issues that may stall implementation.
This may be, for example, an incompatibility of the storage format in older infrastructure or the inability of such infrastructure to process large chunks of data required for geospatial mapping solutions. These usually require custom middleware or system overhauls, which take time, expertise, and extra financial investment.
Besides that, employees accustomed to working with legacy systems may resist the shift to new technologies, citing concerns about the credibility of the steep learning curve. Overcoming such hurdles calls for technical solutions and cultural change within the organization.
3. Ensuring Data Accuracy and Security
Mapping technology in oil and gas is only as good as the data it’s working on to achieve a high level of fidelity. However, this is easier said than done. This area is prone to error from data collection through satellites, drones, and sensors, as well as its analysis and visualization using tools like GIS in oil and gas. Bad data, considering mistakes or safety risks, could cost hundreds of thousands of dollars or worse.
Another major concern lies in data security. In the oil and gas industry, sensitive information passed through the industry covers a wide range, from resource locations to proprietary operation strategies. With the increasing presence of real-time mapping solutions and cloud-based platforms, there is a potential for cyberattacks and information breaches. This calls for companies to apply robust cybersecurity measures concerning geospatial data to ensure accuracy and protection.
Future Trends in Mapping Technology
Mapping solutions in the oil and gas industry are changing to meet new challenges and opportunities. The future will be one innovation after another, not just meeting the requirements that are raising the bar higher and higher but also meeting the demands set by far larger priorities of sustainability, safety, and data-influenced decisions. Here are a few significant trends leading to the transformation of smart infrastructure within this sector:
1. AI and Machine Learning in Geospatial Analysis
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have integrated themselves deep into geospatial mapping solutions to drive efficiencies and accuracy. AI tools analyse the huge amount of oil and gas mapping software data to find patterns for existing trends and automate the most mundane processes.
For example, ML algorithms can identify geological structures containing oil or gas from seismic data, satellite images, and previous drilling records. The insight increases the success rate of exploration while saving costs by avoiding lengthy manual work. AI also increases real-time decisions during drilling and production, thus enabling companies to change course quicker in case circumstances change.
Besides, AI-driven data visualization software facilitates better access to complicated geospatial data by decision-makers. It transforms raw data into insights and visuals through interactive maps and dashboards that can help even a layman better understand infrastructure, environmental risk, and operational inefficiencies.
2. Expanding Use of Real-Time Data and Predictive Mapping
Real-time insights are redefining the oil and gas industries. Advanced sensors, drones, and IoT devices lie at the core of real-time mapping solutions, which provide companies with minute-by-minute details of pipeline conditions, drilling operations, and environmental factors. This becomes critical in industries where small delays or inaccuracies may result in huge problems.
Real-time data enables the instant detection of pipeline leaks or drilling anomalies, helping avert extremely costly accidents and environmental damage. Additionally, predictive mapping utilises historical data and AI algorithms to predict possible future issues even before they strike.
Real-time and predictive mapping combine to create proactive rather than reactive operations with more efficiencies and reduced downtime.
3. Innovative Mapping for Sustainable Resource Management
Sustainability has become the top focus area for nearly all companies engaged in oil and gas operations. Environmental performance will continue to be under increased scrutiny in this sector. Hence, innovative mapping technologies are necessary for companies to reduce their carbon footprint and be considered more responsible operators.
Pipeline mapping technology is continually refined to develop routes that avoid ecologically sensitive areas, reducing habitat destruction and community disruptions. More so, advanced data visualization in oil and gas companies allows them to analyze and communicate the environmental impact of their operations transparently.
The same applies to the latest carbon footprint tracking and green route optimization, which have recently gained significant momentum, especially in logistics and transportation. Companies can make informed decisions on their environmental goals by incorporating sustainability-focused metrics into geographic information systems for oil and gas.
Moreover, technologies such as 3D mapping for oil and gas enable companies to create resilient infrastructures to climatic changes. These tools can cover areas with potential cases of flooding or extreme weather, enabling the firm to plan for future environmental challenges.
How Nextbillion.ai's Mapping Technology Benefits the Oil and Gas Industry
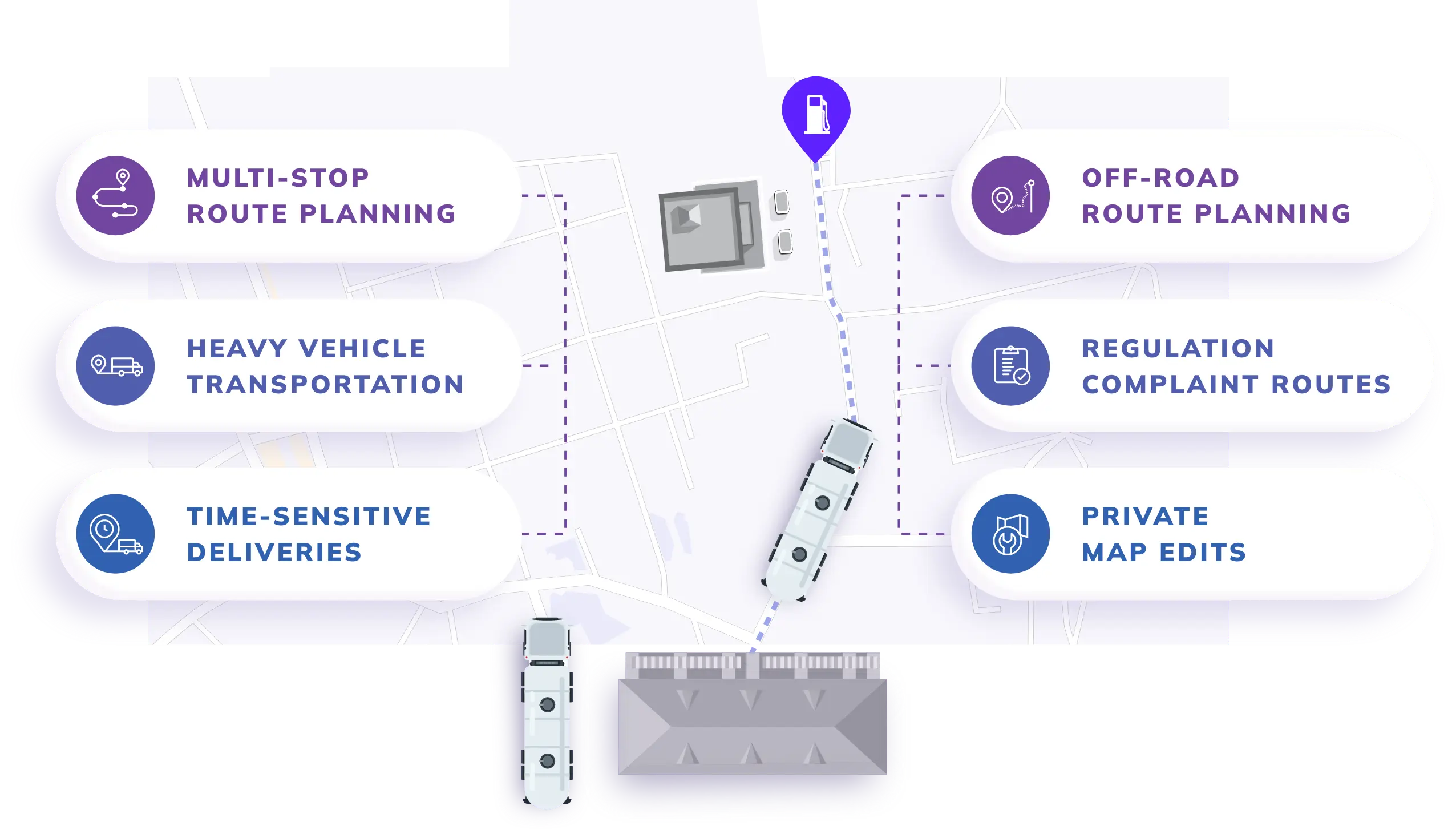
Nextbillion.ai offers tailored mapping solutions that address the unique challenges of the oil and gas sector. NextBillion.ai uses customised maps and tools, such as the Route Optimization API, to plan routes for remote and complex locations efficiently. Here’s how it helps:
- Enhancing Safety: Real-time hazard mapping ensures safer operations, particularly in high-risk environments.
- Reduce Transportation Costs: Precise navigation and fleet optimization reduce fuel consumption and cost to support sustainability goals.
- Asset Tracking: Custom geospatial solutions track assets with a high level of precision, contributing to enhanced operational visibility and control.
- Sustainability Goals: Ecological route optimization in line with environmental objectives will reduce carbon emissions.
From custom editable maps to integrations of live traffic, Nextbillion.ai sets the new benchmark for Oil and Gas mapping software. This geospatial mapping solution has completely empowered companies to make operationally efficient decisions in their core business while prioritising concerns of safety and sustainability.
Conclusion
The integration of mapping technology in oil and gas has really revolutionised the industry, increasing exploration accuracies, operational efficiencies, and environmental compliances. However, challenges remain regarding high costs and legacy integration, but the future looks bright due to advancements in AI, real-time mapping, and sustainability-focused innovations. While it may be true, the right mapping tools can revolutionise how oil and gas companies navigate a noisier, more complex landscape. By using these tools, the industry can ensure its future is safer, more efficient, and sustainable.
FAQs
Drones provide high-resolution, real-time imagery of remote areas, thus allowing efficient pipeline inspections, site surveys, and environmental monitoring.
Real-time mapping provides current data, thus enabling rapid decision-making, hazard detection, and dynamic optimization of operations.
Mapping technology locates ecologically sensitive areas, monitors compliance, and identifies risks such as spills or emissions to protect the environment better.
About Author
Bhavisha Bhatia
Bhavisha Bhatia is a Computer Science graduate with a passion for writing technical blogs that make complex technical concepts engaging and easy to understand. She is intrigued by the technological developments shaping the course of the world and the beautiful nature around us.