Table of Contents
In this era of rapidly expanding eCommerce, last mile delivery is essential to both consumer pleasure and corporate success. Businesses have an advantage in this highly competitive industry if they provide goods on schedule and effectively. However, this also poses serious difficulties for the sector. Businesses may face difficulties with excessive expenses, postponed shipments, and disgruntled clients if they lack the appropriate measures to assess performance.
This article examines the crucial last-mile delivery indicators that small and expanding companies should monitor in order to increase productivity, cut expenses, and give their clients a flawless experience. These insights can assist you in optimizing your operations and scaling efficiently, regardless of whether you are handling deliveries internally or collaborating with other logistics companies.
The Most Crucial KPIs for Last mile Delivery that you should Monitor
Making decisions will be easy from now that you have this understanding about last -mile delivery. Six key performance indicators (KPIs) are listed in this section to help you keep an eye on the effectiveness and well-being of your last-mile delivery business. Select one to three KPIs that are most relevant to your company if you’re just starting out.
1. Success Rate of Deliveries

A key indicator for any delivery company is delivery success rate, which gauges how consistently you fulfill your commitments to clients. Customers demand fresh products that are delivered just as intended, with nothing melted, ruined, or damaged. This is especially important when delivering food, drinks, or other products.
How to Calculate the Success Rate of Deliveries
Number of successful orders ÷ total number of deliveries × 100 equals delivery success.
When an order arrives on schedule, has all the right things, and is in good shape, it is considered a successful delivery. In actuality, consider a delivery successful if it was finished on schedule and the client hasn’t voiced any concerns regarding the quality or correctness of the order.
What good looks like: A minimum of 95% of deliveries should be successful for small food enterprises. Anything less than 90% needs to be addressed right away.
How to Increase the Success of Deliveries
- Use software for route planning to guarantee effective delivery routes.
- Make sure drivers receive accurate customer information (such as access codes) in their delivery notes.
- Utilize real-time tracking to address issues as they come up.
- Teach drivers how to appropriately handle perishable commodities in particular.
- Customers can be informed about delivery windows in a clear and concise manner by using the notifications option in your delivery management software.
- Make sure your products are properly packaged and kept at a consistent temperature.
2. On-time Delivery Rates
The core of the customer experience is a timely delivery. Achieve high customer satisfaction ratings by meeting expectations. On the other hand, delivery delays lead to annoyance and anger, as well as spoilt goods when it comes to food and other perishables.
How to Calculate your Rate of On-time Delivery
The number of on-time deliveries divided by total deliveries is the on-time delivery rate.
What good looks like: At least 90% of deliveries should be made on time by small food delivery services. The goal for restaurant suppliers should be considerably higher—95%+.
How to make Deliveries more Punctual
- Describe what “on-time” means in your particular industry. Is it at the precise time or within the window that was promised?
- To determine reasonable ETAs and delivery schedules, utilize route optimization tools.
- Instead of setting particular timings for deliveries, give your consumers a realistic window of two to three hours.
- Routes should include buffer time to provide for unforeseen delays.
- Monitor delivery in real time to notify clients of any possible hold-ups.
3. Missed Delivery Rates and Unsuccessful Initial Delivery Attempts
Every delivery that is missed costs you twice: once for the first try and again for the second try. This is particularly troublesome for deliveries of perishable food since each delay lowers the quality of the goods.
Typical causes of Unsuccessful Deliveries include:
- The client isn’t at home.
- The address information is not complete or correct.
- There is no way to get to the delivery site.
- Items that are sensitive to temperature cannot be left in a safe location.
Methods for quantifying missed deliveries
The number of unsuccessful initial efforts divided by total deliveries is the missed delivery rate.
What good looks like: The most successful delivery operations maintain a failure rate of less than 3%. Profitability is significantly impacted by anything over 8%.
How to increase the rate of missing deliveries
- Prior to delivery, send out automatic alerts.
- Instead of providing all-day windows, offer specified delivery time intervals.
- To avoid mistakes, use address verification before checking out.
- Provide precise guidelines on what drivers should do in the event that no one is home.
- Provide safe drop options, such as coolers or insulated boxes, for perishable goods.
4. Driver productivity
Your delivery capacity, labor expenses, and profitability are all directly impacted by driver productivity, or the quantity of stops your drivers can make in a day or in a shift. Making the most stops per hour can make the difference between profitable and unsuccessful routes.
How for evaluating the productivity of drivers
Total stops ÷ driver hours equals stops per hour.
How good looks vary greatly depending on where you deliver. Suburban routes may only make three to five stops each hour, but metropolitan routes may make six to eight. To determine your baseline, keep track of your own numbers.
How to increase the productivity of drivers
- Reduce the amount of time you spend traveling between stops by using route optimization software.
- To save time on upcoming deliveries, record delivery notes (gate codes, parking advice).
- Drivers should be assigned to familiar routes and locations.
- To get drivers on the road more quickly, standardize loading processes.
- Give drivers delivery instructions that are clear and manifests that are well-organized.
5. The Price per Delivery
Pricing your delivery service and preserving profitability require knowing your actual cost per delivery. This statistic aids small food enterprises in figuring out delivery costs and minimum order quantities. You can find cost-saving options more readily if you have a better understanding of your cost per delivery.
How to Calculate the Cost per Delivery
Total delivery expenses (fuel, labor, vehicle maintenance, and packing) ÷ the number of deliveries equals the cost per delivery.
What good looks like: Depending on your order values and delivery region density, this can vary greatly. To spot trends, monitor this parameter on a weekly and monthly basis. It’s encouraging when the cost per delivery is going down.
How to Increase the Cost of Delivery
- Reduce the number of miles driven and boost driver efficiency by optimizing routes.
- Deliveries by neighborhood in groups.
- Decide on minimum order quantities for each delivery zone.
- To improve delivery density, take into account delivery days for particular locations.
- Examine your distribution zones and make any adjustments based on profitability.
6. Customer Complaints
Monitoring client feedback helps you spot delivery problems before they have a negative effect on your business’s bottom line. Patterns of complaints frequently highlight issues with your last-mile delivery procedure that could otherwise go overlooked.
How to Evaluate Complaints from Customers
Complaints from customers = total inquiries and grievances ÷ total deliveries
Monitor your complaints and questions by category to maximize this KPI. For instance, the following categories may be the most helpful in a normal food and beverage delivery business:
- Delayed shipment
- Items that are damaged
- Incorrect items
- Where is the order
Aim for complaint rates that are less than 2% of total deliveries. Above all, keep an eye out for patterns and reoccurring problems.
How to Address Consumer Grievances
- Clearly state your delivery windows and turnaround times to establish reasonable expectations for your customers.
- Establish a straightforward way to monitor and classify all consumer input.
- Examine grievances once a week to spot trends.
- Put in place specialized training based on prevalent problems.
- When customers complain, follow up to let them know you’re paying attention.
- Utilize consumer input to enhance route, delivery guidelines, and packaging.
- Send precise ETAs and proof of delivery by using automated consumer notifications.
Tools and Technology for Tracking Last Mile Delivery Metrics
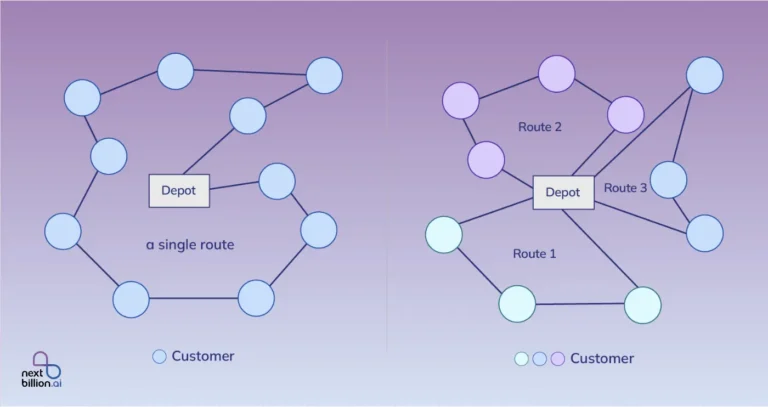
Process improvement, real-time data, and precise tracking are essential for effective last-mile delivery operations. Businesses may lower operating expenses, improve customer satisfaction, and track delivery performance with the correct tools and technology. The following are important technologies for tracking last-mile delivery metrics that small and expanding organizations should take into account.
1. GPS Tracking & Route Optimization Software Goals:
Purpose:
These programs assist companies with real-time delivery vehicle monitoring, route optimization for quicker deliveries, and fuel economy. In order to suggest the best routes, these technologies examine historical data, traffic patterns, and weather trends using artificial intelligence and machine learning.
The Significance of It:
- Cuts down on gasoline expenses and delivery time.
- Real-time driver rerouting helps to avoid delays.
- Aids companies in monitoring driver behavior to increase productivity.
2. Delivery Management Systems (DMS)
Purpose:
A unified platform called a Delivery Management System (DMS) enables companies to manage every aspect of delivery, from order dispatch to shipment tracking and customer relations.
The Significance of it:
- Automates duty assignment to drivers and streamlines order administration.
- Gives delivery information and tracking in real time.
- Increases productivity through integration with POS and eCommerce platforms.
3. Customer Communication & Tracking Tools
Purpose:
By offering tracking links, projected arrival timings, and real-time delivery updates, customer communication solutions assist companies in enhancing the customer experience. By informing clients, these tools decrease the number of missed deliveries.
The Significance of It:
- Decreases complaints and questions from customers regarding the status of their orders.
- Increases openness and fosters consumer trust.
- Reduces the number of unsuccessful deliveries by making sure clients are available to accept orders.
4. Proof of Delivery (POD) Solutions
Purpose:
By obtaining delivery confirmation via signatures, images, or barcode scans, Proof of Delivery (POD) technology guarantees responsibility and minimizes disputes.
The Significance of It:
- Verifies that the correct person received the package.
- Reduces false allegations of non-delivery.
- Enhances documentation for legal and customer support needs.
5. Dashboards for Data Analytics and Reporting
Purpose:
The goal of data analytics tools is to assist companies in tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) including average delivery time, cost per delivery, and delivery success rate. These resources offer insightful information to boost operational effectiveness.
The Significance of It:
- Finds patterns and locations where delivery operations need to be improved.
- Aids companies in making data-driven choices.
- Analyzes fuel use, driver effectiveness, and customer happiness to optimize expenses.
Using Metrics for Continuous Improvement
A business may find it useful to monitor its progress in order to determine how to keep improving its operations. Metrics for continuous improvement are just one of many techniques to monitor a company’s development. Understanding the various metrics used to gauge development can help you make sure a business is improving over time, which is particularly beneficial if it has well-defined objectives. This article examines seven different kinds of metrics for continuous improvement that businesses may use to monitor their progress.
Monitoring last-mile delivery metrics involves more than just gathering data; it also entails using insights to promote ongoing development. Companies can use these KPIs in the methods listed below:
1. Locate and fix bottlenecks
Finding persistent delays and inefficiencies can be aided by examining delivery time, success rates, and driver performance. Then, businesses can: Further optimize delivery routes. Effectively distribute resources according to times of peak demand. To increase efficiency, attend to drivers’ training needs.
2. Enhance Customer Experience
Data on customer satisfaction, such as reviews and ratings, can be utilized to: Enhance proactive changes in communication tactics. Provide a range of delivery choices according to client preferences. Improved cooperation will result in fewer unsuccessful delivery attempts.
3. Lower Operating Expenses
Businesses can find cost-saving options like fuel-efficient routing by using cost-per-delivery indicators. Cut down on delivery staff idle time. Streamline processes by automating repetitive procedures.
4. Improve Forecasting and Planning
Using historical data on delivery success rates and seasonal variations can help enhance the accuracy of demand predictions. Assist in labor planning to account for changes in the volume of deliveries. Help businesses scale their operations efficiently.
5. Ensure Compliance and Sustainability
By keeping an eye on environmental impact measures, businesses can implement more ecologically friendly delivery options, including electric trucks. Reduce emissions by optimizing delivery scheduling. Observe the carbon footprint regulations.
Ensure Reliable, Cost-Effective, and On-Time Last-Mile Delivery with Nextbillion.ai
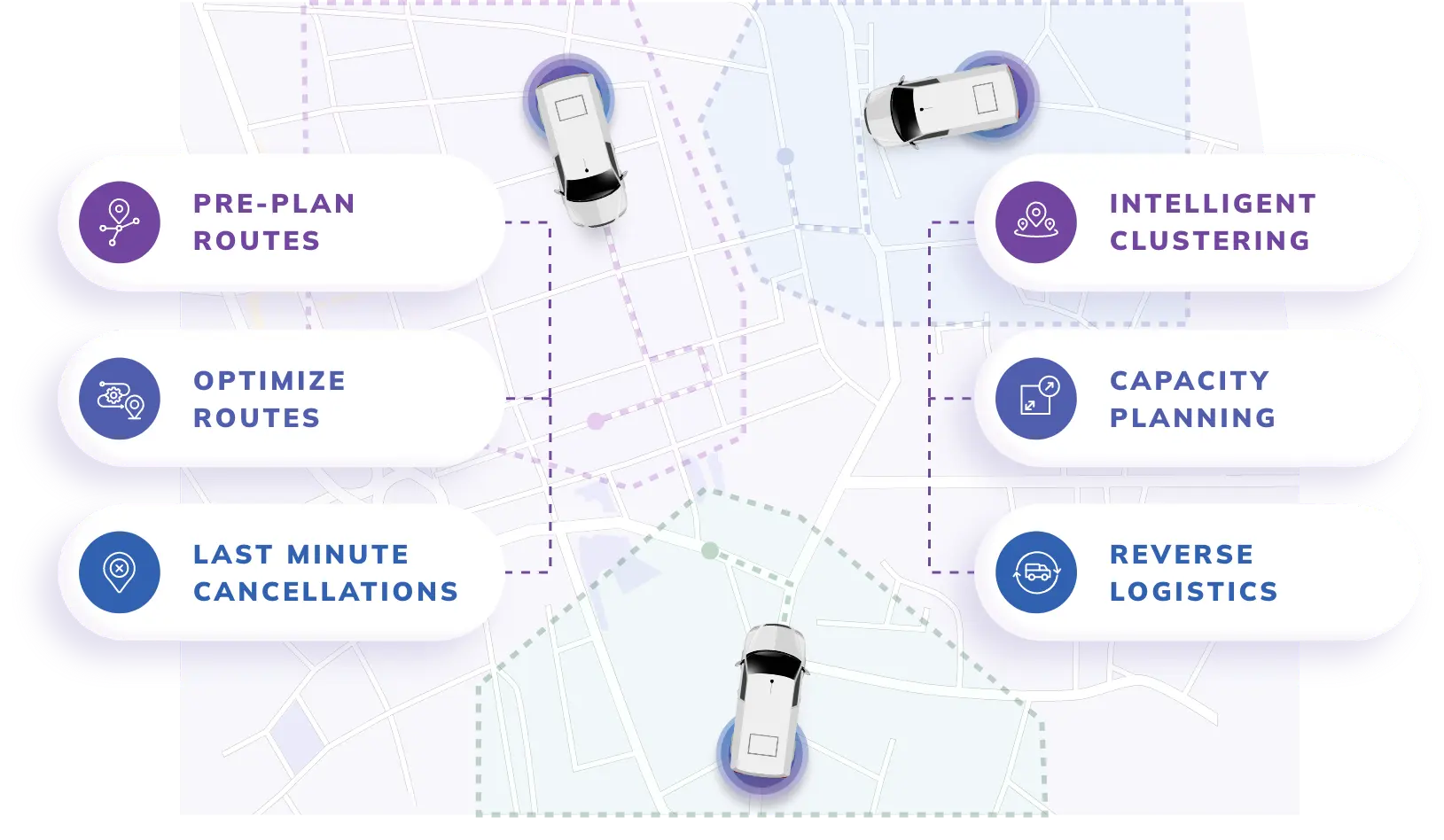
Use Nextbillion.ai to optimize and streamline your last-mile delivery processes. Our intelligent logistics solutions guarantee quicker, more effective deliveries by streamlining zone-based allocation, capacity planning, and pre-planning.
Why Choose Nextbillion.ai?
Improved Pre-Planning: Use insights driven by AI to predict demand, allocate resources optimally, and avoid inefficiencies.
Smooth Capacity Planning: Reduce expenses by effectively managing fleet utilization and distributing loads across available resources.
Zone-Based Allocation: By carefully dividing distribution zones, this method shortens travel times and boosts delivery effectiveness.
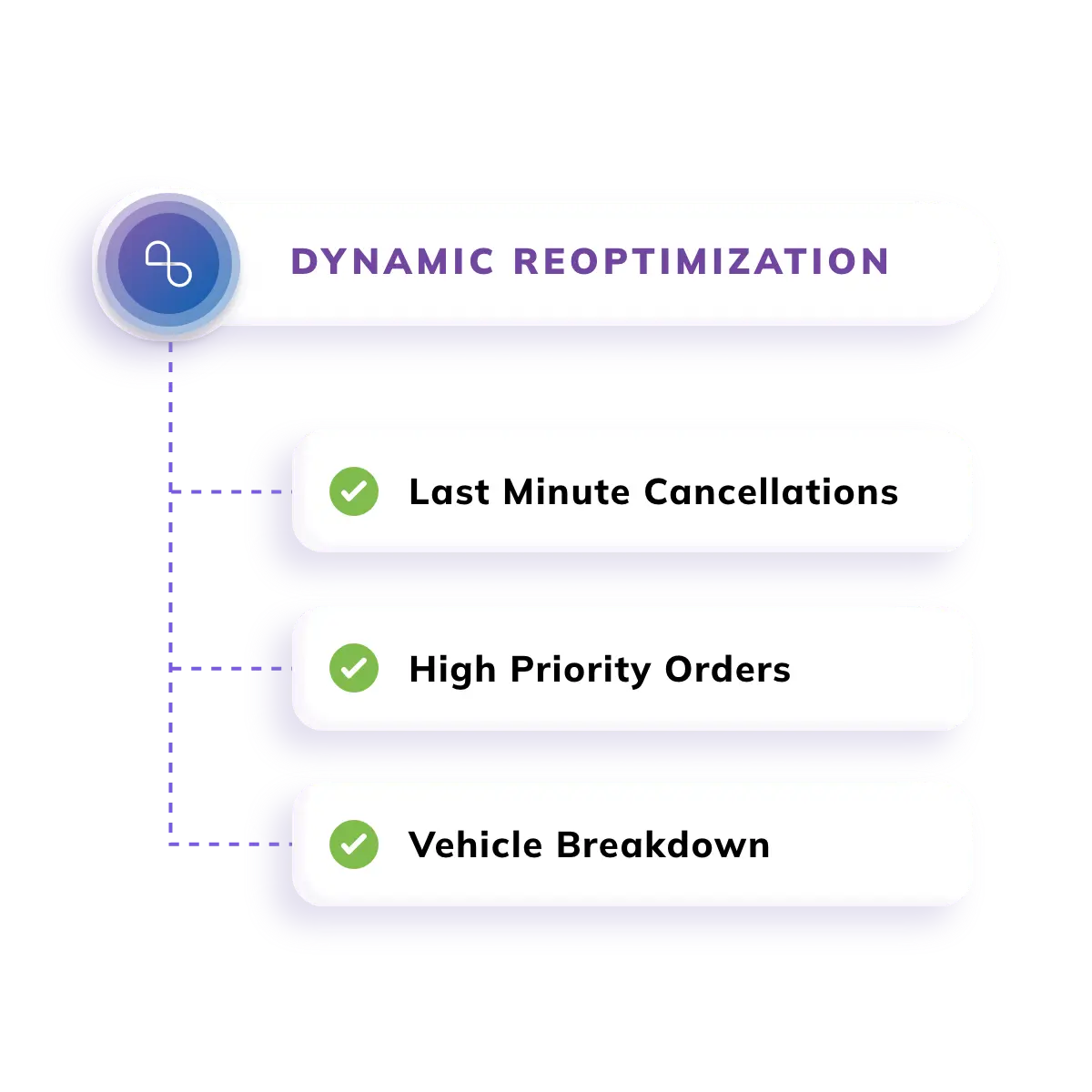
Dynamic Route Reoptimization: To guarantee on-time and dependable deliveries, adjust to real-time variables like traffic, weather, and route constraints.
Improved Operational Flexibility: Use real-time decision-making and intelligent automation to stay ahead of disruptions.
Businesses may increase dependability, reduce costs, and surpass customer expectations in last-mile delivery by utilizing Nextbillion.ai.
Conclusion
For small and growing businesses, tracking essential last mile delivery metrics is crucial for optimizing operations, improving customer satisfaction, and maintaining cost efficiency. By focusing on key metrics such as delivery time, success rate, customer satisfaction, and operational costs, businesses can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions. Leveraging technology like GPS tracking, route optimization software, and AI-powered analytics enables better visibility and control over delivery operations.
As competition in the eCommerce and logistics space continues to grow, businesses that prioritize efficient last-mile delivery will gain a competitive edge. By continuously monitoring performance and implementing strategic improvements, small businesses can enhance service reliability, build customer trust, and scale their operations effectively in an increasingly demanding market.
About Author
Divya Nair
Divya is a dedicated Technical Content Writer with experience of two years in the industry. Her expertise spans various forms of writing, including blogs and website content.